Brief Summary
Reference
-
Spanish Ministry of Economy, Industry and Competitiveness, TEC2016-76795-C6-4-R, 01/2017-06/2020, 146.047 euros
"Flexible management of 5G services oriented to support urban critical situations (5G-CITY)", P. Ameigeiras, J. M. Lopez-Soler, 2020
close
@researchproject{5gcity, code={TEC2016-76795-C6-4-R}, title={Flexible management of 5G services oriented to support urban critical situations (5G-CITY)}, org={Spanish Ministry of Economy, Industry and Competitiveness}, type={national}, author={P. Ameigeiras and J. M. Lopez-Soler}, year=2020, month=6, date1={01/2017}, date2={06/2020}, funding={146.047 euros}, logo="http://wimunet.ugr.es/assets/img/research/projects/ministerio-de-economia-industria-y-competitividad.jpg", url0="http://wimunet.ugr.es/projects/5gcity.php"}
close
Spanish Ministry of Economy, Industry and Competitiveness, TEC2016-76795-C6-4-R, 01/2017-06/2020, 146.047 euros
"Flexible management of 5G services oriented to support urban critical situations (5G-CITY)", P. Ameigeiras, J. M. Lopez-Soler, 2020close
@researchproject{5gcity, code={TEC2016-76795-C6-4-R}, title={Flexible management of 5G services oriented to support urban critical situations (5G-CITY)}, org={Spanish Ministry of Economy, Industry and Competitiveness}, type={national}, author={P. Ameigeiras and J. M. Lopez-Soler}, year=2020, month=6, date1={01/2017}, date2={06/2020}, funding={146.047 euros}, logo="http://wimunet.ugr.es/assets/img/research/projects/ministerio-de-economia-industria-y-competitividad.jpg", url0="http://wimunet.ugr.es/projects/5gcity.php"}
close
This national project (TEC2016-76795-C6-4-R) is titled "Flexible management of 5G services oriented to support urban critical situations" (5G-CITY). It started in 2017 and ended in June 2020.
The main web page of this project is available at https://genwebv4.upc.edu/5gcity/en
Description
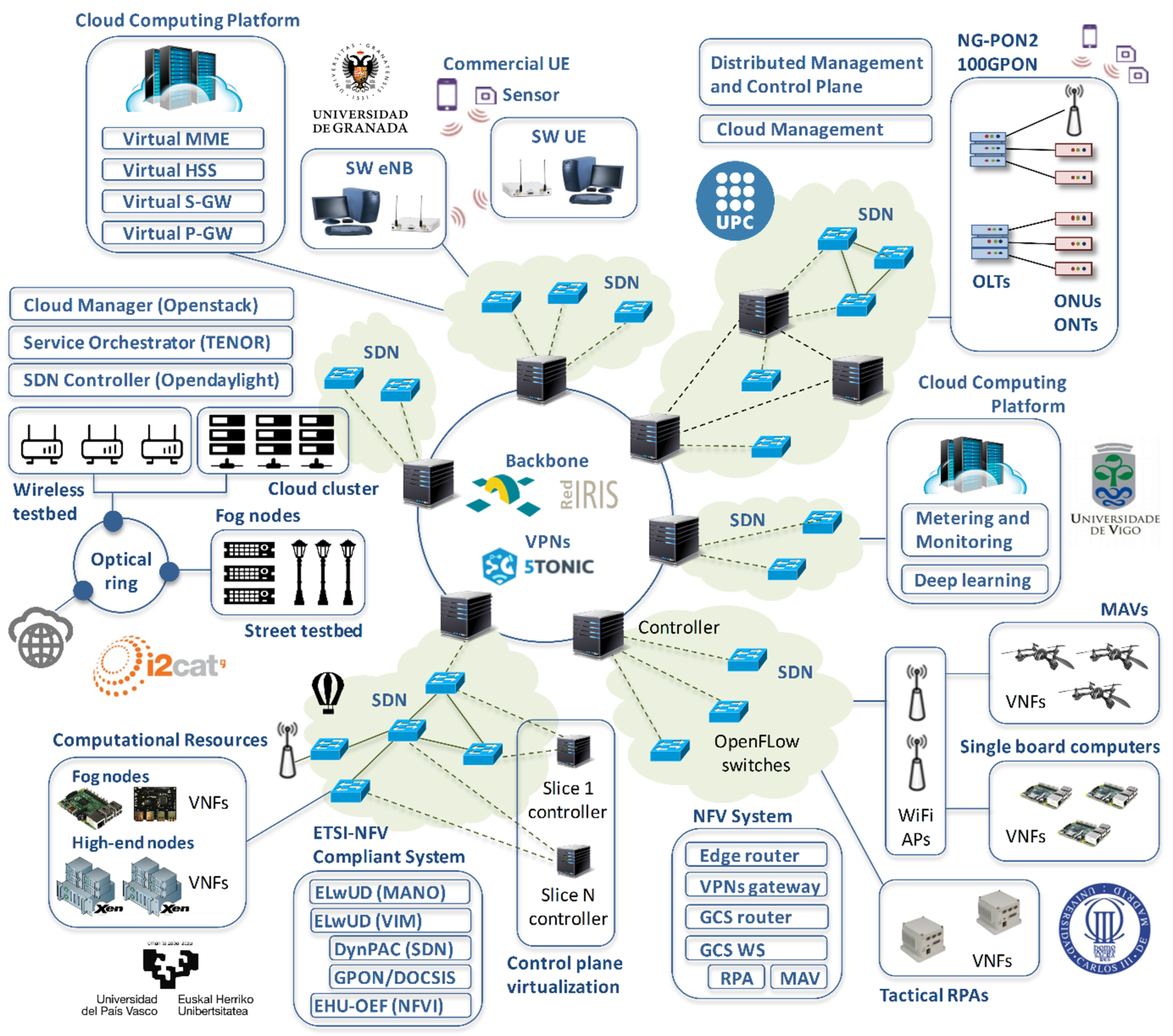
The research project Adaptive Management of 5G Services to Support Critical Events in Cities (5GCity) is a granted project of the Spanish's Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad through the National Programme for Fostering Excellence in Scientific and Technical Research, Sub-Programme "Proyectos de I+D orientados a Retos de la Sociedad". This is a collaborative project with the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC), the i2CAT Foundation (i2CAT), the Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M), the Universidad de Granada (UGR) and the Universidad del Pais Vasco (Euskal Herriko Unibertsitatea) (UPV/EHU).
The general objective of this project is to provide adequate support for the smart city paradigm in the most challenging scenarios, namely unexpected, critical events involving a large number of citizens concentrating in a small geographic area. The approach is to develop an adaptive solution to control 5G technologies and configure communication services, maintaining low-latency requirements, adequate scalability characteristics and high dependability.
The following picture summarizes the 5G-CITY's testbed, which expands over the different partners' premises.

Publications
Journals
-
Collision Avoidance Resource Allocation for LoRaWAN
Sensors, 21 (4), 2 2021, DOI: 10.3390/s21041218. (IF=3.576, Q2)
"Collision Avoidance Resource Allocation for LoRaWAN", Natalia Chinchilla-Romero, Jorge Navarro-Ortiz, Pablo Munoz, Pablo Ameigeiras, Sensors, 21 (4), 2021. DOI: 10.3390/s21041218
close
The number of connected IoT devices is significantly increasing and it is expected to reach more than two dozens of billions of IoT connections in the coming years. Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWAN) have become very relevant for this new paradigm due to features such as large coverage and low power consumption. One of the most appealing technologies among these networks is LoRaWAN. Although it may be considered as one of the most mature LPWAN platforms, there are still open gaps such as its capacity limitations. For this reason, this work proposes a collision avoidance resource allocation algorithm named the Collision Avoidance Resource Allocation (CARA) algorithm with the objective of significantly increase system capacity. CARA leverages the multichannel structure and the orthogonality of spreading factors in LoRaWAN networks to avoid collisions among devices. Simulation results show that, assuming ideal radio link conditions, our proposal outperforms in 95.2% the capacity of a standard LoRaWAN network and increases the capacity by almost 40% assuming a realistic propagation model. In addition, it has been verified that CARA devices can coexist with LoRaWAN traditional devices, thus allowing the simultaneous transmissions of both types of devices. Moreover, a proof-of-concept has been implemented using commercial equipment in order to check the feasibility and the correct operation of our solution.
close
@ARTICLE{s21041218,
AUTHOR = {Chinchilla-Romero, Natalia and Navarro-Ortiz, Jorge and Munoz, Pablo and Ameigeiras, Pablo},
TITLE = {Collision Avoidance Resource Allocation for {LoRaWAN}},
JOURNAL = {Sensors},
VOLUME = {21},
YEAR = {2021},
month=2,
NUMBER = {4},
ARTICLE-NUMBER = {1218},
ISSN = {1424-8220},
ABSTRACT = {The number of connected IoT devices is significantly increasing and it is expected to reach more than two dozens of billions of IoT connections in the coming years. Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWAN) have become very relevant for this new paradigm due to features such as large coverage and low power consumption. One of the most appealing technologies among these networks is {LoRaWAN}. Although it may be considered as one of the most mature LPWAN platforms, there are still open gaps such as its capacity limitations. For this reason, this work proposes a collision avoidance resource allocation algorithm named the Collision Avoidance Resource Allocation (CARA) algorithm with the objective of significantly increase system capacity. CARA leverages the multichannel structure and the orthogonality of spreading factors in {LoRaWAN} networks to avoid collisions among devices. Simulation results show that, assuming ideal radio link conditions, our proposal outperforms in 95.2% the capacity of a standard {LoRaWAN} network and increases the capacity by almost 40% assuming a realistic propagation model. In addition, it has been verified that CARA devices can coexist with {LoRaWAN} traditional devices, thus allowing the simultaneous transmissions of both types of devices. Moreover, a proof-of-concept has been implemented using commercial equipment in order to check the feasibility and the correct operation of our solution.},
DOI = {10.3390/s21041218},
impact = {(IF=3.576, Q2)},
pdf = {https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/67701},
project = {artemis|5gcity|5gclarity}
}
close
-
Dynamic Resource Provisioning of a Scalable E2E Network Slicing Orchestration System
IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 19 (11), pp. 2594-2608, Nov 2020, DOI: 10.1109/TMC.2019.2930059. (IF=5.112, Q1)
"Dynamic Resource Provisioning of a Scalable E2E Network Slicing Orchestration System", I. Afolabi, J. Prados-Garzon, M. Bagaa, T. Taleb, P. Ameigeiras, IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 19 (11), pp. 2594-2608, 2020. DOI: 10.1109/TMC.2019.2930059
close
@ARTICLE{afolabi19, author={I. {Afolabi} and J. {Prados-Garzon} and M. {Bagaa} and T. {Taleb} and P. {Ameigeiras}}, journal={IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing}, title={Dynamic Resource Provisioning of a Scalable E2E Network Slicing Orchestration System}, year={2020}, volume={19}, number={11}, pages={2594-2608}, doi={10.1109/TMC.2019.2930059}, ISSN={1558-0660}, month={Nov}, impact={(IF=5.112, Q1)}, project={5gcity}, pdf={https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/59687}
}
close
-
A Complete LTE Mathematical Framework for the Network Slice Planning of the EPC
IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 19 (1), pp. 1-14, Jan 2020, DOI: 10.1109/TMC.2018.2890235. (IF=5.112, Q1)
"A Complete LTE Mathematical Framework for the Network Slice Planning of the EPC", J. Prados-Garzon, A. Laghrissi, M. Bagaa, T. Taleb, J. M. Lopez-Soler, IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 19 (1), pp. 1-14, 2020. DOI: 10.1109/TMC.2018.2890235
close
5G is the next telecommunications standards that will enable the sharing of physical infrastructures to provision ultra shortlatency applications, mobile broadband services, Internet of Things, etc. Network slicing is the virtualization technique that is expected to achieve that, as it can allow logical networks to run on top of a common physical infrastructure and ensure service level agreement requirements for different services and applications. In this vein, our paper proposes a novel and complete solution for planning network slices of the LTE EPC, tailored for the enhanced Mobile BroadBand use case. The solution defines a framework which consists of: i) an abstraction of the LTE workload generation process, ii) a compound traffic model, iii) performance models of the whole LTE network, and iv) an algorithm to jointly perform the resource dimensioning and network embedding. Our results show that the aggregated signaling generation is a Poisson process and the data traffic exhibits self-similarity and long-range-dependence features. The proposed performance models for the LTE network rely on these results. We formulate the joint optimization problem of resources dimensioning and embedding of a virtualized EPC and propose a heuristic to solve it. By using simulation tools, we validate the proper operation of our solution.
close
@ARTICLE{8603789, author={J. {Prados-Garzon} and A. {Laghrissi} and M. {Bagaa} and T. {Taleb} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler}}, journal={IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing}, title={A Complete LTE Mathematical Framework for the Network Slice Planning of the EPC}, year={2020}, volume={19}, number={1}, pages={1-14}, abstract={5G is the next telecommunications standards that will enable the sharing of physical infrastructures to provision ultra shortlatency applications, mobile broadband services, Internet of Things, etc. Network slicing is the virtualization technique that is expected to achieve that, as it can allow logical networks to run on top of a common physical infrastructure and ensure service level agreement requirements for different services and applications. In this vein, our paper proposes a novel and complete solution for planning network slices of the LTE EPC, tailored for the enhanced Mobile BroadBand use case. The solution defines a framework which consists of: i) an abstraction of the LTE workload generation process, ii) a compound traffic model, iii) performance models of the whole LTE network, and iv) an algorithm to jointly perform the resource dimensioning and network embedding. Our results show that the aggregated signaling generation is a Poisson process and the data traffic exhibits self-similarity and long-range-dependence features. The proposed performance models for the LTE network rely on these results. We formulate the joint optimization problem of resources dimensioning and embedding of a virtualized EPC and propose a heuristic to solve it. By using simulation tools, we validate the proper operation of our solution.}, keywords={Long Term Evolution;Planning;Quality of service;Analytical models;Logic gates;Optimization;5G mobile communication;LTE;EPC;network slicing;NFV;softwarized networks;mobile networks;traffic characterization;resources dimensioning;network embedding}, doi={10.1109/TMC.2018.2890235}, ISSN={1558-0660}, month={Jan}, impact={(IF=5.112, Q1)}, project={5gcity}}
close
-
A Survey on 5G Usage Scenarios and Traffic Models
IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 22 (2), pp. 905-929, 2 2020, DOI: 10.1109/COMST.2020.2971781. (IF=23.7, Q1)
"A Survey on 5G Usage Scenarios and Traffic Models", J. Navarro-Ortiz, P. Romero-Diaz, S. Sendra, P. Ameigeiras, J. J. Ramos-Munoz, J. M. Lopez-Soler, IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 22 (2), pp. 905-929, 2020. DOI: 10.1109/COMST.2020.2971781
close
@Article{8985528, author={J. {Navarro-Ortiz} and P. {Romero-Diaz} and S. {Sendra} and P. {Ameigeiras} and J. J. {Ramos-Munoz} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler}}, journal={{IEEE} Communications Surveys Tutorials}, title={A Survey on 5G Usage Scenarios and Traffic Models}, year={2020}, month=2, volume={22}, number={2}, pages={905-929}, doi={10.1109/COMST.2020.2971781}, project="artemis|5gclarity|5gcity", impact = {(IF=23.7, Q1)}, pdf={https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/59687}}
close
-
Harmonizing 3GPP and NFV Description Models: Providing Customized RAN Slices in 5G Networks
IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 14 (4), pp. 64-75, Dec 2019, DOI: 10.1109/MVT.2019.2936168. (IF=7.921, Q1)
"Harmonizing 3GPP and NFV Description Models: Providing Customized RAN Slices in 5G Networks", O. Adamuz-Hinojosa, P. Munoz, J. Ordonez-Lucena, J. J. Ramos-Munoz, J. M. Lopez-Soler, IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 14 (4), pp. 64-75, 2019. DOI: 10.1109/MVT.2019.2936168
close
The standardization of radio access networks (RANs) in mobile networks has traditionally been led by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). However, the emergence of RAN slicing has introduced new aspects that fall outside the 3GPP scope. Among them, network virtualization enables the particularization of multiple behaviors over a common physical infrastructure. Using virtualized network functions (VNFs) that comprise customized radio functionalities, each virtualized RAN (i.e., RAN slice) could meet its specific requirements. Although the 3GPP specifies the description model to manage RAN slices, it can neither particularize the behavior of a RAN slice nor leverage the network function virtualization (NFV) descriptors to define how its VNFs can accommodate its spatial and temporal traffic demands. In this article, we propose a description model that harmonizes 3GPP and the European Telecommunication Standard Institute (ETSI)-NFV Group viewpoints to manage RAN slices. The proposed model enables the translation of RAN slice requirements into customized, virtualized radio functionalities defined through NFV descriptors. To clarify this proposal, we provide an example describing three RAN slices with disruptive requirements following our solution.
close
@ARTICLE{8854309, author={O. {Adamuz-Hinojosa} and P. {Munoz} and J. {Ordonez-Lucena} and J. J. {Ramos-Munoz} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler}}, journal={IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine}, title={Harmonizing 3GPP and NFV Description Models: Providing Customized RAN Slices in 5G Networks}, year={2019}, volume={14}, number={4}, pages={64-75}, abstract={The standardization of radio access networks (RANs) in mobile networks has traditionally been led by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). However, the emergence of RAN slicing has introduced new aspects that fall outside the 3GPP scope. Among them, network virtualization enables the particularization of multiple behaviors over a common physical infrastructure. Using virtualized network functions (VNFs) that comprise customized radio functionalities, each virtualized RAN (i.e., RAN slice) could meet its specific requirements. Although the 3GPP specifies the description model to manage RAN slices, it can neither particularize the behavior of a RAN slice nor leverage the network function virtualization (NFV) descriptors to define how its VNFs can accommodate its spatial and temporal traffic demands. In this article, we propose a description model that harmonizes 3GPP and the European Telecommunication Standard Institute (ETSI)-NFV Group viewpoints to manage RAN slices. The proposed model enables the translation of RAN slice requirements into customized, virtualized radio functionalities defined through NFV descriptors. To clarify this proposal, we provide an example describing three RAN slices with disruptive requirements following our solution.}, keywords={3GPP;Biological system modeling;5G mobile communication;Virtualization;Vehicular and wireless technologies;Radio access networks}, doi={10.1109/MVT.2019.2936168}, ISSN={1556-6080}, month={Dec},impact={(IF=7.921, Q1)}, project={5gcity}, pdf={https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/68200}}
close
-
Performance Modeling of Softwarized Network Services Based on Queuing Theory With Experimental Validation
IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 20 (4), pp. 1558-1573, 12 2019, DOI: 10.1109/TMC.2019.2962488. (IF=5.112, Q1)
"Performance Modeling of Softwarized Network Services Based on Queuing Theory With Experimental Validation", J. Prados-Garzon, P. Ameigeiras, J. J. Ramos-Munoz, J. Navarro-Ortiz, P. Andres-Maldonado, J. M. Lopez-Soler, IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 20 (4), pp. 1558-1573, 2019. DOI: 10.1109/TMC.2019.2962488
close
@Article{8943161, author={J. {Prados-Garzon} and P. {Ameigeiras} and J. J. {Ramos-Munoz} and J. {Navarro-Ortiz} and P. {Andres-Maldonado} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler}}, journal={{IEEE} Transactions on Mobile Computing}, title={Performance Modeling of Softwarized Network Services Based on Queuing Theory With Experimental Validation}, year={2019}, month={12}, volume={20}, number={4}, pages={1558-1573}, doi={10.1109/TMC.2019.2962488}, project="5gclarity|5gcity", impact={(IF=5.112, Q1)}, pdf={https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/59700}}
close
-
Analytical Modeling and Experimental Validation of NB-IoT Device Energy Consumption
IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6 (3), pp. 5691-5701, June 2019, DOI: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2904802. (IF=9.936, Q1)
"Analytical Modeling and Experimental Validation of NB-IoT Device Energy Consumption", P. Andres-Maldonado, M. Lauridsen, P. Ameigeiras, J. M. Lopez-Soler, IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6 (3), pp. 5691-5701, 2019. DOI: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2904802
close
The recent standardization of 3GPP Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT) paves the way to support low-power wide-area (LPWA) use cases in cellular networks. NB-IoT design goals are extended coverage, low power and low cost devices, and massive connections. As a new radio access technology, it is necessary to analyze the possibilities NB-IoT provides to support different traffic and coverage needs. In this paper, we propose and validate an NB-IoT energy consumption model. The analytical model is based on a Markov chain. For the validation, an experimental setup is used to measure the energy consumption of two commercial NB-IoT user equipments (UEs) connected to a base station emulator. The evaluation is done considering three test cases. The comparison of the model and measurements is done in terms of the estimated battery lifetime and the latency needed to finish the control plane procedure. The conducted evaluation shows the analytical model performs well, obtaining a maximum relative error of the battery lifetime estimation between the model and the measurements of 21% for an assumed interarrival time (IAT) of 6 min.
close
@ARTICLE{8666720, author={P. {Andres-Maldonado} and M. {Lauridsen} and P. {Ameigeiras} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler}}, journal={IEEE Internet of Things Journal}, title={Analytical Modeling and Experimental Validation of NB-IoT Device Energy Consumption}, year={2019}, volume={6}, number={3}, pages={5691-5701}, abstract={The recent standardization of 3GPP Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT) paves the way to support low-power wide-area (LPWA) use cases in cellular networks. NB-IoT design goals are extended coverage, low power and low cost devices, and massive connections. As a new radio access technology, it is necessary to analyze the possibilities NB-IoT provides to support different traffic and coverage needs. In this paper, we propose and validate an NB-IoT energy consumption model. The analytical model is based on a Markov chain. For the validation, an experimental setup is used to measure the energy consumption of two commercial NB-IoT user equipments (UEs) connected to a base station emulator. The evaluation is done considering three test cases. The comparison of the model and measurements is done in terms of the estimated battery lifetime and the latency needed to finish the control plane procedure. The conducted evaluation shows the analytical model performs well, obtaining a maximum relative error of the battery lifetime estimation between the model and the measurements of 21% for an assumed interarrival time (IAT) of 6 min.}, keywords={Internet of Things;Energy consumption;Analytical models;Batteries;Narrowband;Downlink;Battery charge measurement;Analytical model;control plane (CP);energy consumption;latency;narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT)}, doi={10.1109/JIOT.2019.2904802}, ISSN={2327-4662}, month={June},impact={(IF=9.936, Q1)}, project={5gcity}}
close
-
Testbeds for Future Wireless Networks
Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2019, pp. 1-2, June 2019, DOI: 10.1155/2019/2382471. (IF=1.819, Q3)
-
A LoRaWAN Testbed Design for Supporting Critical Situations: Prototype and Evaluation
Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2019, pp. 1-13, Feb 2019, DOI: 10.1155/2019/1684906. (IF=1.819, Q3)
-
An Analytical Performance Evaluation Framework for NB-IoT
IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6 (4), pp. 7232-7240, 4 2019, DOI: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2915349. (IF=9.936, Q1)
"An Analytical Performance Evaluation Framework for NB-IoT", P. Andres-Maldonado, P. Ameigeiras, J. Prados-Garzon, J. Navarro-Ortiz, J. M. Lopez-Soler, IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6 (4), pp. 7232-7240, 2019. DOI: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2915349
close
@Article{8708311, author={P. {Andres-Maldonado} and P. {Ameigeiras} and J. {Prados-Garzon} and J. {Navarro-Ortiz} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler}}, journal={{IEEE} Internet of Things Journal}, title={An Analytical Performance Evaluation Framework for NB-IoT}, month=4, year={2019}, volume={6}, number={4}, pages={7232-7240}, doi={10.1109/JIOT.2019.2915349}, impact={(IF=9.936, Q1)}, project={5gcity}, pdf={https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/68246}}
close
-
Automated Network Service Scaling in NFV: Concepts, Mechanisms and Scaling Workflow
IEEE Communications Magazine, 56 (7), pp. 162-169, July 2018, DOI: 10.1109/MCOM.2018.1701336. (IF=10.356, Q1)
"Automated Network Service Scaling in NFV: Concepts, Mechanisms and Scaling Workflow", Oscar Adamuz-Hinojosa, Jose Ordonez-Lucena, Pablo Ameigeiras, Juan J. Ramos-Munoz, Diego Lopez, Jesus Folgueira, IEEE Communications Magazine, 56 (7), pp. 162-169, 2018. DOI: 10.1109/MCOM.2018.1701336
close
Next-generation systems are anticipated to be digital platforms supporting innovative services with rapidly changing traffic patterns. To cope with this dynamicity in a cost-efficient manner, operators need advanced service management capabilities such as those provided by NFV. NFV enables operators to scale network services with higher granularity and agility than today. To this end, automation is key. In search of this automation, ETSI has defined a reference NFV framework that makes use of model-driven templates called NSDs to operate network services. For the scaling operation, an NSD defines a discrete set of instantiation levels among which a network service instance can be resized throughout its life cycle. Thus, the design of these levels is key for ensuring effective scaling. In this article, we provide an overview of the automation of the network service scaling operation in NFV, addressing the options and boundaries introduced by ETSI normative specifications. We start by providing a description of the NSD structure, focusing on how instantiation levels are constructed. For illustrative purposes, we propose an NSD for a representative network service. This NSD includes different instantiation levels that enable different ways to automatically scale this network service. Then we show the different scaling procedures the NFV framework has available, and how it may automate their triggering. Finally, we propose an ETSI-compliant workflow to describe in detail a representative scaling procedure. This workflow clarifies the interactions and information exchanges between the functional blocks in the NFV framework when performing the scaling operation.
close
@ARTICLE{OscarScaling2018,
author={Adamuz-Hinojosa, Oscar and Ordonez-Lucena, Jose and Ameigeiras, Pablo and Ramos-Munoz, Juan J. and Lopez, Diego and Folgueira, Jesus},
journal={IEEE Communications Magazine},
title={Automated Network Service Scaling in NFV: Concepts, Mechanisms and Scaling Workflow},
year={2018},
volume={56},
number={7},
pages={162-169},
abstract={Next-generation systems are anticipated to be digital platforms supporting innovative services with rapidly changing traffic patterns. To cope with this dynamicity in a cost-efficient manner, operators need advanced service management capabilities such as those provided by NFV. NFV enables operators to scale network services with higher granularity and agility than today. To this end, automation is key. In search of this automation, ETSI has defined a reference NFV framework that makes use of model-driven templates called NSDs to operate network services. For the scaling operation, an NSD defines a discrete set of instantiation levels among which a network service instance can be resized throughout its life cycle. Thus, the design of these levels is key for ensuring effective scaling. In this article, we provide an overview of the automation of the network service scaling operation in NFV, addressing the options and boundaries introduced by ETSI normative specifications. We start by providing a description of the NSD structure, focusing on how instantiation levels are constructed. For illustrative purposes, we propose an NSD for a representative network service. This NSD includes different instantiation levels that enable different ways to automatically scale this network service. Then we show the different scaling procedures the NFV framework has available, and how it may automate their triggering. Finally, we propose an ETSI-compliant workflow to describe in detail a representative scaling procedure. This workflow clarifies the interactions and information exchanges between the functional blocks in the NFV framework when performing the scaling operation.},
keywords={},
doi={10.1109/MCOM.2018.1701336},
ISSN={1558-1896},
month={July},
impact = {(IF=10.356, Q1)},
project={5gcity}, pdf={https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/68205}
}
close
-
Self-Dimensioning and Planning of Small Cell Capacity in Multitenant 5G Networks
IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 67 (5), pp. 4552-4564, May 2018, DOI: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2793418. (IF=5.33, Q1)
"Self-Dimensioning and Planning of Small Cell Capacity in Multitenant 5G Networks", P. Munoz, O. Sallent, J. Perez-Romero, IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 67 (5), pp. 4552-4564, 2018. DOI: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2793418
close
An important concept in the fifth generation of mobile networks is multitenancy, which allows diverse operators sharing the same wireless infrastructure. To support this feature in conjunction with the challenging performance requirements of future networks, more automated and faster planning of the required radio capacity is needed. Likewise, installing small cells is an effective resource to provide greater performance and capacity to both indoor and outdoor places. This paper proposes a new framework for automated cell planning in multitenant small cell networks. In particular, taking advantage of the available network data, a set of detailed planning specifications over time and space domains are generated in order to meet the contracted capacity by each tenant. Then, the network infrastructure and configuration are updated according to an algorithm that considers different actions such as adding/removing channels and adding or relocating small cells. The simulation results show the effectiveness of various methods to derive the planning specifications depending on the correlation between the tenant's and network's traffic demands.
close
@ARTICLE{8259010,
author={P. {Munoz} and O. {Sallent} and J. {Perez-Romero}},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology},
title={Self-Dimensioning and Planning of Small Cell Capacity in Multitenant 5G Networks},
year={2018},
volume={67},
number={5},
pages={4552-4564},
abstract={An important concept in the fifth generation of mobile networks is multitenancy, which allows diverse operators sharing the same wireless infrastructure. To support this feature in conjunction with the challenging performance requirements of future networks, more automated and faster planning of the required radio capacity is needed. Likewise, installing small cells is an effective resource to provide greater performance and capacity to both indoor and outdoor places. This paper proposes a new framework for automated cell planning in multitenant small cell networks. In particular, taking advantage of the available network data, a set of detailed planning specifications over time and space domains are generated in order to meet the contracted capacity by each tenant. Then, the network infrastructure and configuration are updated according to an algorithm that considers different actions such as adding/removing channels and adding or relocating small cells. The simulation results show the effectiveness of various methods to derive the planning specifications depending on the correlation between the tenant's and network's traffic demands.},
keywords={5G mobile communication;cellular radio;telecommunication network planning;telecommunication traffic;wireless channels;fifth generation mobile network;multitenant 5G networks;tenant traffic demands;network traffic demands;space domains;multitenant small cell networks;automated cell planning;outdoor places;indoor places;required radio capacity;automated planning;wireless infrastructure;Planning;5G mobile communication;Capacity planning;Mobile computing;Macrocell networks;Capacity planning;dimensioning;5G networks;multi-tenancy;small cells;SON},
doi={10.1109/TVT.2018.2793418},
ISSN={1939-9359},
month={May},
impact = {(IF=5.33, Q1)},
project = {related5gcity}, pdf={https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/68230}
}
close
-
Integration of LoRaWAN and 4G/5G for the Industrial Internet of Things
IEEE Communications Magazine, 56 (2), pp. 60-67, 2 2018, DOI: 10.1109/MCOM.2018.1700625. (IF=9.27, Q1)
"Integration of LoRaWAN and 4G/5G for the Industrial Internet of Things", J. Navarro-Ortiz, S. Sendra, P. Ameigeiras, J. M. Lopez-Soler, IEEE Communications Magazine, 56 (2), pp. 60-67, 2018. DOI: 10.1109/MCOM.2018.1700625
close
@Article{8291115, author={J. {Navarro-Ortiz} and S. {Sendra} and P. {Ameigeiras} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler}}, journal={{IEEE} Communications Magazine}, title={Integration of {LoRaWAN} and 4G/5G for the Industrial Internet of Things}, year={2018}, month=2, volume={56}, number={2}, pages={60-67}, doi={10.1109/MCOM.2018.1700625}, pdf={https://hdl.handle.net/10481/86867}, impact={(IF=9.27, Q1)}, project={5gcity}}
close
-
Network Slicing for 5G with SDN/NFV: Concepts, Architectures, and Challenges
IEEE Communications Magazine, 55 (5), pp. 80-87, 2017, DOI: 10.1109/MCOM.2017.1600935. (IF=9.270, Q1)
"Network Slicing for 5G with SDN/NFV: Concepts, Architectures, and Challenges", Jose Ordonez-Lucena, Pablo Ameigeiras, Diego Lopez, Juan J. Ramos-Munoz, Javier Lorca, Jesus Folgueira, IEEE Communications Magazine, 55 (5), pp. 80-87, 2017. DOI: 10.1109/MCOM.2017.1600935
close
@ARTICLE{7926921,
author={Ordonez-Lucena, Jose and Ameigeiras, Pablo and Lopez, Diego and Ramos-Munoz, Juan J. and Lorca, Javier and Folgueira, Jesus},
journal={IEEE Communications Magazine},
title={Network Slicing for 5G with SDN/NFV: Concepts, Architectures, and Challenges},
year={2017},
volume={55},
number={5},
pages={80-87},
doi={10.1109/MCOM.2017.1600935},
impact={(IF=9.270, Q1)}, project={5gcity}, pdf={https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/45368}}
close
Collision Avoidance Resource Allocation for LoRaWANSensors, 21 (4), 2 2021, DOI: 10.3390/s21041218. (IF=3.576, Q2)
"Collision Avoidance Resource Allocation for LoRaWAN", Natalia Chinchilla-Romero, Jorge Navarro-Ortiz, Pablo Munoz, Pablo Ameigeiras, Sensors, 21 (4), 2021. DOI: 10.3390/s21041218close
The number of connected IoT devices is significantly increasing and it is expected to reach more than two dozens of billions of IoT connections in the coming years. Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWAN) have become very relevant for this new paradigm due to features such as large coverage and low power consumption. One of the most appealing technologies among these networks is LoRaWAN. Although it may be considered as one of the most mature LPWAN platforms, there are still open gaps such as its capacity limitations. For this reason, this work proposes a collision avoidance resource allocation algorithm named the Collision Avoidance Resource Allocation (CARA) algorithm with the objective of significantly increase system capacity. CARA leverages the multichannel structure and the orthogonality of spreading factors in LoRaWAN networks to avoid collisions among devices. Simulation results show that, assuming ideal radio link conditions, our proposal outperforms in 95.2% the capacity of a standard LoRaWAN network and increases the capacity by almost 40% assuming a realistic propagation model. In addition, it has been verified that CARA devices can coexist with LoRaWAN traditional devices, thus allowing the simultaneous transmissions of both types of devices. Moreover, a proof-of-concept has been implemented using commercial equipment in order to check the feasibility and the correct operation of our solution.close
@ARTICLE{s21041218,
AUTHOR = {Chinchilla-Romero, Natalia and Navarro-Ortiz, Jorge and Munoz, Pablo and Ameigeiras, Pablo},
TITLE = {Collision Avoidance Resource Allocation for {LoRaWAN}},
JOURNAL = {Sensors},
VOLUME = {21},
YEAR = {2021},
month=2,
NUMBER = {4},
ARTICLE-NUMBER = {1218},
ISSN = {1424-8220},
ABSTRACT = {The number of connected IoT devices is significantly increasing and it is expected to reach more than two dozens of billions of IoT connections in the coming years. Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWAN) have become very relevant for this new paradigm due to features such as large coverage and low power consumption. One of the most appealing technologies among these networks is {LoRaWAN}. Although it may be considered as one of the most mature LPWAN platforms, there are still open gaps such as its capacity limitations. For this reason, this work proposes a collision avoidance resource allocation algorithm named the Collision Avoidance Resource Allocation (CARA) algorithm with the objective of significantly increase system capacity. CARA leverages the multichannel structure and the orthogonality of spreading factors in {LoRaWAN} networks to avoid collisions among devices. Simulation results show that, assuming ideal radio link conditions, our proposal outperforms in 95.2% the capacity of a standard {LoRaWAN} network and increases the capacity by almost 40% assuming a realistic propagation model. In addition, it has been verified that CARA devices can coexist with {LoRaWAN} traditional devices, thus allowing the simultaneous transmissions of both types of devices. Moreover, a proof-of-concept has been implemented using commercial equipment in order to check the feasibility and the correct operation of our solution.},
DOI = {10.3390/s21041218},
impact = {(IF=3.576, Q2)},
pdf = {https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/67701},
project = {artemis|5gcity|5gclarity}
}
close
Dynamic Resource Provisioning of a Scalable E2E Network Slicing Orchestration SystemIEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 19 (11), pp. 2594-2608, Nov 2020, DOI: 10.1109/TMC.2019.2930059. (IF=5.112, Q1)
"Dynamic Resource Provisioning of a Scalable E2E Network Slicing Orchestration System", I. Afolabi, J. Prados-Garzon, M. Bagaa, T. Taleb, P. Ameigeiras, IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 19 (11), pp. 2594-2608, 2020. DOI: 10.1109/TMC.2019.2930059close
@ARTICLE{afolabi19, author={I. {Afolabi} and J. {Prados-Garzon} and M. {Bagaa} and T. {Taleb} and P. {Ameigeiras}}, journal={IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing}, title={Dynamic Resource Provisioning of a Scalable E2E Network Slicing Orchestration System}, year={2020}, volume={19}, number={11}, pages={2594-2608}, doi={10.1109/TMC.2019.2930059}, ISSN={1558-0660}, month={Nov}, impact={(IF=5.112, Q1)}, project={5gcity}, pdf={https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/59687}
}
close
A Complete LTE Mathematical Framework for the Network Slice Planning of the EPCIEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 19 (1), pp. 1-14, Jan 2020, DOI: 10.1109/TMC.2018.2890235. (IF=5.112, Q1)
"A Complete LTE Mathematical Framework for the Network Slice Planning of the EPC", J. Prados-Garzon, A. Laghrissi, M. Bagaa, T. Taleb, J. M. Lopez-Soler, IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 19 (1), pp. 1-14, 2020. DOI: 10.1109/TMC.2018.2890235close
5G is the next telecommunications standards that will enable the sharing of physical infrastructures to provision ultra shortlatency applications, mobile broadband services, Internet of Things, etc. Network slicing is the virtualization technique that is expected to achieve that, as it can allow logical networks to run on top of a common physical infrastructure and ensure service level agreement requirements for different services and applications. In this vein, our paper proposes a novel and complete solution for planning network slices of the LTE EPC, tailored for the enhanced Mobile BroadBand use case. The solution defines a framework which consists of: i) an abstraction of the LTE workload generation process, ii) a compound traffic model, iii) performance models of the whole LTE network, and iv) an algorithm to jointly perform the resource dimensioning and network embedding. Our results show that the aggregated signaling generation is a Poisson process and the data traffic exhibits self-similarity and long-range-dependence features. The proposed performance models for the LTE network rely on these results. We formulate the joint optimization problem of resources dimensioning and embedding of a virtualized EPC and propose a heuristic to solve it. By using simulation tools, we validate the proper operation of our solution.close
@ARTICLE{8603789, author={J. {Prados-Garzon} and A. {Laghrissi} and M. {Bagaa} and T. {Taleb} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler}}, journal={IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing}, title={A Complete LTE Mathematical Framework for the Network Slice Planning of the EPC}, year={2020}, volume={19}, number={1}, pages={1-14}, abstract={5G is the next telecommunications standards that will enable the sharing of physical infrastructures to provision ultra shortlatency applications, mobile broadband services, Internet of Things, etc. Network slicing is the virtualization technique that is expected to achieve that, as it can allow logical networks to run on top of a common physical infrastructure and ensure service level agreement requirements for different services and applications. In this vein, our paper proposes a novel and complete solution for planning network slices of the LTE EPC, tailored for the enhanced Mobile BroadBand use case. The solution defines a framework which consists of: i) an abstraction of the LTE workload generation process, ii) a compound traffic model, iii) performance models of the whole LTE network, and iv) an algorithm to jointly perform the resource dimensioning and network embedding. Our results show that the aggregated signaling generation is a Poisson process and the data traffic exhibits self-similarity and long-range-dependence features. The proposed performance models for the LTE network rely on these results. We formulate the joint optimization problem of resources dimensioning and embedding of a virtualized EPC and propose a heuristic to solve it. By using simulation tools, we validate the proper operation of our solution.}, keywords={Long Term Evolution;Planning;Quality of service;Analytical models;Logic gates;Optimization;5G mobile communication;LTE;EPC;network slicing;NFV;softwarized networks;mobile networks;traffic characterization;resources dimensioning;network embedding}, doi={10.1109/TMC.2018.2890235}, ISSN={1558-0660}, month={Jan}, impact={(IF=5.112, Q1)}, project={5gcity}}
close
A Survey on 5G Usage Scenarios and Traffic ModelsIEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 22 (2), pp. 905-929, 2 2020, DOI: 10.1109/COMST.2020.2971781. (IF=23.7, Q1)
"A Survey on 5G Usage Scenarios and Traffic Models", J. Navarro-Ortiz, P. Romero-Diaz, S. Sendra, P. Ameigeiras, J. J. Ramos-Munoz, J. M. Lopez-Soler, IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 22 (2), pp. 905-929, 2020. DOI: 10.1109/COMST.2020.2971781close
@Article{8985528, author={J. {Navarro-Ortiz} and P. {Romero-Diaz} and S. {Sendra} and P. {Ameigeiras} and J. J. {Ramos-Munoz} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler}}, journal={{IEEE} Communications Surveys Tutorials}, title={A Survey on 5G Usage Scenarios and Traffic Models}, year={2020}, month=2, volume={22}, number={2}, pages={905-929}, doi={10.1109/COMST.2020.2971781}, project="artemis|5gclarity|5gcity", impact = {(IF=23.7, Q1)}, pdf={https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/59687}}
close
Harmonizing 3GPP and NFV Description Models: Providing Customized RAN Slices in 5G NetworksIEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 14 (4), pp. 64-75, Dec 2019, DOI: 10.1109/MVT.2019.2936168. (IF=7.921, Q1)
"Harmonizing 3GPP and NFV Description Models: Providing Customized RAN Slices in 5G Networks", O. Adamuz-Hinojosa, P. Munoz, J. Ordonez-Lucena, J. J. Ramos-Munoz, J. M. Lopez-Soler, IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 14 (4), pp. 64-75, 2019. DOI: 10.1109/MVT.2019.2936168close
The standardization of radio access networks (RANs) in mobile networks has traditionally been led by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). However, the emergence of RAN slicing has introduced new aspects that fall outside the 3GPP scope. Among them, network virtualization enables the particularization of multiple behaviors over a common physical infrastructure. Using virtualized network functions (VNFs) that comprise customized radio functionalities, each virtualized RAN (i.e., RAN slice) could meet its specific requirements. Although the 3GPP specifies the description model to manage RAN slices, it can neither particularize the behavior of a RAN slice nor leverage the network function virtualization (NFV) descriptors to define how its VNFs can accommodate its spatial and temporal traffic demands. In this article, we propose a description model that harmonizes 3GPP and the European Telecommunication Standard Institute (ETSI)-NFV Group viewpoints to manage RAN slices. The proposed model enables the translation of RAN slice requirements into customized, virtualized radio functionalities defined through NFV descriptors. To clarify this proposal, we provide an example describing three RAN slices with disruptive requirements following our solution.close
@ARTICLE{8854309, author={O. {Adamuz-Hinojosa} and P. {Munoz} and J. {Ordonez-Lucena} and J. J. {Ramos-Munoz} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler}}, journal={IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine}, title={Harmonizing 3GPP and NFV Description Models: Providing Customized RAN Slices in 5G Networks}, year={2019}, volume={14}, number={4}, pages={64-75}, abstract={The standardization of radio access networks (RANs) in mobile networks has traditionally been led by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). However, the emergence of RAN slicing has introduced new aspects that fall outside the 3GPP scope. Among them, network virtualization enables the particularization of multiple behaviors over a common physical infrastructure. Using virtualized network functions (VNFs) that comprise customized radio functionalities, each virtualized RAN (i.e., RAN slice) could meet its specific requirements. Although the 3GPP specifies the description model to manage RAN slices, it can neither particularize the behavior of a RAN slice nor leverage the network function virtualization (NFV) descriptors to define how its VNFs can accommodate its spatial and temporal traffic demands. In this article, we propose a description model that harmonizes 3GPP and the European Telecommunication Standard Institute (ETSI)-NFV Group viewpoints to manage RAN slices. The proposed model enables the translation of RAN slice requirements into customized, virtualized radio functionalities defined through NFV descriptors. To clarify this proposal, we provide an example describing three RAN slices with disruptive requirements following our solution.}, keywords={3GPP;Biological system modeling;5G mobile communication;Virtualization;Vehicular and wireless technologies;Radio access networks}, doi={10.1109/MVT.2019.2936168}, ISSN={1556-6080}, month={Dec},impact={(IF=7.921, Q1)}, project={5gcity}, pdf={https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/68200}}
close
Performance Modeling of Softwarized Network Services Based on Queuing Theory With Experimental ValidationIEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 20 (4), pp. 1558-1573, 12 2019, DOI: 10.1109/TMC.2019.2962488. (IF=5.112, Q1)
"Performance Modeling of Softwarized Network Services Based on Queuing Theory With Experimental Validation", J. Prados-Garzon, P. Ameigeiras, J. J. Ramos-Munoz, J. Navarro-Ortiz, P. Andres-Maldonado, J. M. Lopez-Soler, IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 20 (4), pp. 1558-1573, 2019. DOI: 10.1109/TMC.2019.2962488close
@Article{8943161, author={J. {Prados-Garzon} and P. {Ameigeiras} and J. J. {Ramos-Munoz} and J. {Navarro-Ortiz} and P. {Andres-Maldonado} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler}}, journal={{IEEE} Transactions on Mobile Computing}, title={Performance Modeling of Softwarized Network Services Based on Queuing Theory With Experimental Validation}, year={2019}, month={12}, volume={20}, number={4}, pages={1558-1573}, doi={10.1109/TMC.2019.2962488}, project="5gclarity|5gcity", impact={(IF=5.112, Q1)}, pdf={https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/59700}}
close
Analytical Modeling and Experimental Validation of NB-IoT Device Energy ConsumptionIEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6 (3), pp. 5691-5701, June 2019, DOI: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2904802. (IF=9.936, Q1)
"Analytical Modeling and Experimental Validation of NB-IoT Device Energy Consumption", P. Andres-Maldonado, M. Lauridsen, P. Ameigeiras, J. M. Lopez-Soler, IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6 (3), pp. 5691-5701, 2019. DOI: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2904802close
The recent standardization of 3GPP Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT) paves the way to support low-power wide-area (LPWA) use cases in cellular networks. NB-IoT design goals are extended coverage, low power and low cost devices, and massive connections. As a new radio access technology, it is necessary to analyze the possibilities NB-IoT provides to support different traffic and coverage needs. In this paper, we propose and validate an NB-IoT energy consumption model. The analytical model is based on a Markov chain. For the validation, an experimental setup is used to measure the energy consumption of two commercial NB-IoT user equipments (UEs) connected to a base station emulator. The evaluation is done considering three test cases. The comparison of the model and measurements is done in terms of the estimated battery lifetime and the latency needed to finish the control plane procedure. The conducted evaluation shows the analytical model performs well, obtaining a maximum relative error of the battery lifetime estimation between the model and the measurements of 21% for an assumed interarrival time (IAT) of 6 min.close
@ARTICLE{8666720, author={P. {Andres-Maldonado} and M. {Lauridsen} and P. {Ameigeiras} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler}}, journal={IEEE Internet of Things Journal}, title={Analytical Modeling and Experimental Validation of NB-IoT Device Energy Consumption}, year={2019}, volume={6}, number={3}, pages={5691-5701}, abstract={The recent standardization of 3GPP Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT) paves the way to support low-power wide-area (LPWA) use cases in cellular networks. NB-IoT design goals are extended coverage, low power and low cost devices, and massive connections. As a new radio access technology, it is necessary to analyze the possibilities NB-IoT provides to support different traffic and coverage needs. In this paper, we propose and validate an NB-IoT energy consumption model. The analytical model is based on a Markov chain. For the validation, an experimental setup is used to measure the energy consumption of two commercial NB-IoT user equipments (UEs) connected to a base station emulator. The evaluation is done considering three test cases. The comparison of the model and measurements is done in terms of the estimated battery lifetime and the latency needed to finish the control plane procedure. The conducted evaluation shows the analytical model performs well, obtaining a maximum relative error of the battery lifetime estimation between the model and the measurements of 21% for an assumed interarrival time (IAT) of 6 min.}, keywords={Internet of Things;Energy consumption;Analytical models;Batteries;Narrowband;Downlink;Battery charge measurement;Analytical model;control plane (CP);energy consumption;latency;narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT)}, doi={10.1109/JIOT.2019.2904802}, ISSN={2327-4662}, month={June},impact={(IF=9.936, Q1)}, project={5gcity}}
close
Testbeds for Future Wireless NetworksWireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2019, pp. 1-2, June 2019, DOI: 10.1155/2019/2382471. (IF=1.819, Q3)
A LoRaWAN Testbed Design for Supporting Critical Situations: Prototype and EvaluationWireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2019, pp. 1-13, Feb 2019, DOI: 10.1155/2019/1684906. (IF=1.819, Q3)
An Analytical Performance Evaluation Framework for NB-IoTIEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6 (4), pp. 7232-7240, 4 2019, DOI: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2915349. (IF=9.936, Q1)
"An Analytical Performance Evaluation Framework for NB-IoT", P. Andres-Maldonado, P. Ameigeiras, J. Prados-Garzon, J. Navarro-Ortiz, J. M. Lopez-Soler, IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6 (4), pp. 7232-7240, 2019. DOI: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2915349close
@Article{8708311, author={P. {Andres-Maldonado} and P. {Ameigeiras} and J. {Prados-Garzon} and J. {Navarro-Ortiz} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler}}, journal={{IEEE} Internet of Things Journal}, title={An Analytical Performance Evaluation Framework for NB-IoT}, month=4, year={2019}, volume={6}, number={4}, pages={7232-7240}, doi={10.1109/JIOT.2019.2915349}, impact={(IF=9.936, Q1)}, project={5gcity}, pdf={https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/68246}}
close
Automated Network Service Scaling in NFV: Concepts, Mechanisms and Scaling WorkflowIEEE Communications Magazine, 56 (7), pp. 162-169, July 2018, DOI: 10.1109/MCOM.2018.1701336. (IF=10.356, Q1)
"Automated Network Service Scaling in NFV: Concepts, Mechanisms and Scaling Workflow", Oscar Adamuz-Hinojosa, Jose Ordonez-Lucena, Pablo Ameigeiras, Juan J. Ramos-Munoz, Diego Lopez, Jesus Folgueira, IEEE Communications Magazine, 56 (7), pp. 162-169, 2018. DOI: 10.1109/MCOM.2018.1701336close
Next-generation systems are anticipated to be digital platforms supporting innovative services with rapidly changing traffic patterns. To cope with this dynamicity in a cost-efficient manner, operators need advanced service management capabilities such as those provided by NFV. NFV enables operators to scale network services with higher granularity and agility than today. To this end, automation is key. In search of this automation, ETSI has defined a reference NFV framework that makes use of model-driven templates called NSDs to operate network services. For the scaling operation, an NSD defines a discrete set of instantiation levels among which a network service instance can be resized throughout its life cycle. Thus, the design of these levels is key for ensuring effective scaling. In this article, we provide an overview of the automation of the network service scaling operation in NFV, addressing the options and boundaries introduced by ETSI normative specifications. We start by providing a description of the NSD structure, focusing on how instantiation levels are constructed. For illustrative purposes, we propose an NSD for a representative network service. This NSD includes different instantiation levels that enable different ways to automatically scale this network service. Then we show the different scaling procedures the NFV framework has available, and how it may automate their triggering. Finally, we propose an ETSI-compliant workflow to describe in detail a representative scaling procedure. This workflow clarifies the interactions and information exchanges between the functional blocks in the NFV framework when performing the scaling operation.close
@ARTICLE{OscarScaling2018,
author={Adamuz-Hinojosa, Oscar and Ordonez-Lucena, Jose and Ameigeiras, Pablo and Ramos-Munoz, Juan J. and Lopez, Diego and Folgueira, Jesus},
journal={IEEE Communications Magazine},
title={Automated Network Service Scaling in NFV: Concepts, Mechanisms and Scaling Workflow},
year={2018},
volume={56},
number={7},
pages={162-169},
abstract={Next-generation systems are anticipated to be digital platforms supporting innovative services with rapidly changing traffic patterns. To cope with this dynamicity in a cost-efficient manner, operators need advanced service management capabilities such as those provided by NFV. NFV enables operators to scale network services with higher granularity and agility than today. To this end, automation is key. In search of this automation, ETSI has defined a reference NFV framework that makes use of model-driven templates called NSDs to operate network services. For the scaling operation, an NSD defines a discrete set of instantiation levels among which a network service instance can be resized throughout its life cycle. Thus, the design of these levels is key for ensuring effective scaling. In this article, we provide an overview of the automation of the network service scaling operation in NFV, addressing the options and boundaries introduced by ETSI normative specifications. We start by providing a description of the NSD structure, focusing on how instantiation levels are constructed. For illustrative purposes, we propose an NSD for a representative network service. This NSD includes different instantiation levels that enable different ways to automatically scale this network service. Then we show the different scaling procedures the NFV framework has available, and how it may automate their triggering. Finally, we propose an ETSI-compliant workflow to describe in detail a representative scaling procedure. This workflow clarifies the interactions and information exchanges between the functional blocks in the NFV framework when performing the scaling operation.},
keywords={},
doi={10.1109/MCOM.2018.1701336},
ISSN={1558-1896},
month={July},
impact = {(IF=10.356, Q1)},
project={5gcity}, pdf={https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/68205}
}
close
Self-Dimensioning and Planning of Small Cell Capacity in Multitenant 5G NetworksIEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 67 (5), pp. 4552-4564, May 2018, DOI: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2793418. (IF=5.33, Q1)
"Self-Dimensioning and Planning of Small Cell Capacity in Multitenant 5G Networks", P. Munoz, O. Sallent, J. Perez-Romero, IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 67 (5), pp. 4552-4564, 2018. DOI: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2793418close
An important concept in the fifth generation of mobile networks is multitenancy, which allows diverse operators sharing the same wireless infrastructure. To support this feature in conjunction with the challenging performance requirements of future networks, more automated and faster planning of the required radio capacity is needed. Likewise, installing small cells is an effective resource to provide greater performance and capacity to both indoor and outdoor places. This paper proposes a new framework for automated cell planning in multitenant small cell networks. In particular, taking advantage of the available network data, a set of detailed planning specifications over time and space domains are generated in order to meet the contracted capacity by each tenant. Then, the network infrastructure and configuration are updated according to an algorithm that considers different actions such as adding/removing channels and adding or relocating small cells. The simulation results show the effectiveness of various methods to derive the planning specifications depending on the correlation between the tenant's and network's traffic demands.close
@ARTICLE{8259010,
author={P. {Munoz} and O. {Sallent} and J. {Perez-Romero}},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology},
title={Self-Dimensioning and Planning of Small Cell Capacity in Multitenant 5G Networks},
year={2018},
volume={67},
number={5},
pages={4552-4564},
abstract={An important concept in the fifth generation of mobile networks is multitenancy, which allows diverse operators sharing the same wireless infrastructure. To support this feature in conjunction with the challenging performance requirements of future networks, more automated and faster planning of the required radio capacity is needed. Likewise, installing small cells is an effective resource to provide greater performance and capacity to both indoor and outdoor places. This paper proposes a new framework for automated cell planning in multitenant small cell networks. In particular, taking advantage of the available network data, a set of detailed planning specifications over time and space domains are generated in order to meet the contracted capacity by each tenant. Then, the network infrastructure and configuration are updated according to an algorithm that considers different actions such as adding/removing channels and adding or relocating small cells. The simulation results show the effectiveness of various methods to derive the planning specifications depending on the correlation between the tenant's and network's traffic demands.},
keywords={5G mobile communication;cellular radio;telecommunication network planning;telecommunication traffic;wireless channels;fifth generation mobile network;multitenant 5G networks;tenant traffic demands;network traffic demands;space domains;multitenant small cell networks;automated cell planning;outdoor places;indoor places;required radio capacity;automated planning;wireless infrastructure;Planning;5G mobile communication;Capacity planning;Mobile computing;Macrocell networks;Capacity planning;dimensioning;5G networks;multi-tenancy;small cells;SON},
doi={10.1109/TVT.2018.2793418},
ISSN={1939-9359},
month={May},
impact = {(IF=5.33, Q1)},
project = {related5gcity}, pdf={https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/68230}
}
close
Integration of LoRaWAN and 4G/5G for the Industrial Internet of ThingsIEEE Communications Magazine, 56 (2), pp. 60-67, 2 2018, DOI: 10.1109/MCOM.2018.1700625. (IF=9.27, Q1)
"Integration of LoRaWAN and 4G/5G for the Industrial Internet of Things", J. Navarro-Ortiz, S. Sendra, P. Ameigeiras, J. M. Lopez-Soler, IEEE Communications Magazine, 56 (2), pp. 60-67, 2018. DOI: 10.1109/MCOM.2018.1700625close
@Article{8291115, author={J. {Navarro-Ortiz} and S. {Sendra} and P. {Ameigeiras} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler}}, journal={{IEEE} Communications Magazine}, title={Integration of {LoRaWAN} and 4G/5G for the Industrial Internet of Things}, year={2018}, month=2, volume={56}, number={2}, pages={60-67}, doi={10.1109/MCOM.2018.1700625}, pdf={https://hdl.handle.net/10481/86867}, impact={(IF=9.27, Q1)}, project={5gcity}}
close
Network Slicing for 5G with SDN/NFV: Concepts, Architectures, and ChallengesIEEE Communications Magazine, 55 (5), pp. 80-87, 2017, DOI: 10.1109/MCOM.2017.1600935. (IF=9.270, Q1)
"Network Slicing for 5G with SDN/NFV: Concepts, Architectures, and Challenges", Jose Ordonez-Lucena, Pablo Ameigeiras, Diego Lopez, Juan J. Ramos-Munoz, Javier Lorca, Jesus Folgueira, IEEE Communications Magazine, 55 (5), pp. 80-87, 2017. DOI: 10.1109/MCOM.2017.1600935close
@ARTICLE{7926921,
author={Ordonez-Lucena, Jose and Ameigeiras, Pablo and Lopez, Diego and Ramos-Munoz, Juan J. and Lorca, Javier and Folgueira, Jesus},
journal={IEEE Communications Magazine},
title={Network Slicing for 5G with SDN/NFV: Concepts, Architectures, and Challenges},
year={2017},
volume={55},
number={5},
pages={80-87},
doi={10.1109/MCOM.2017.1600935},
impact={(IF=9.270, Q1)}, project={5gcity}, pdf={https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/45368}}
close
Conferences & Workshops
-
Sharing gNB components in RAN slicing: A perspective from 3GPP/NFV standards
2019 IEEE Conference on Standards for Communications and Networking (CSCN), pp. 1-7, October 2019, DOI: 10.1109/CSCN.2019.8931318.
"Sharing gNB components in RAN slicing: A perspective from 3GPP/NFV standards", O. Adamuz-Hinojosa, P. Munoz, P. Ameigeiras, J. M. Lopez-Soler, "2019 IEEE Conference on Standards for Communications and Networking (CSCN)", pp. 1-7, 2019. DOI: 10.1109/CSCN.2019.8931318
close
To implement the next Generation NodeBs (gNBs) that are present in every Radio Access Network (RAN) slice subnet, Network Function Virtualization (NFV) enables the deployment of some of the gNB components as Virtual Networks Functions (VNFs). Deploying individual VNF instances for these components could guarantee the customization of each RAN slice subnet. However, due to the multiplicity of VNFs, the required amount of virtual resources will be greater compared to the case where a single VNF instance carries the aggregated traffic of all the RAN slice subnets. Sharing gNB components between RAN slice subnets could optimize the trade-off between customization, isolation and resource utilization. In this article, we shed light on the key aspects in the Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP)/NFV standards for sharing gNB components. First, we identify four possible scenarios for sharing gNB components. Then, we analyze the impact of sharing on the customization level of each RAN slice subnet. Later, we determine the main factors that enable isolation between RAN slice subnets. Finally, we propose a 3GPP/NFV-based description model to define the lifecycle management of shared gNB components.
close
@INPROCEEDINGS{8931318, author={O. {Adamuz-Hinojosa} and P. {Munoz} and P. {Ameigeiras} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler}}, booktitle={2019 IEEE Conference on Standards for Communications and Networking (CSCN)}, title={Sharing gNB components in RAN slicing: A perspective from 3GPP/NFV standards}, year={2019}, volume={}, number={}, pages={1-7}, abstract={To implement the next Generation NodeBs (gNBs) that are present in every Radio Access Network (RAN) slice subnet, Network Function Virtualization (NFV) enables the deployment of some of the gNB components as Virtual Networks Functions (VNFs). Deploying individual VNF instances for these components could guarantee the customization of each RAN slice subnet. However, due to the multiplicity of VNFs, the required amount of virtual resources will be greater compared to the case where a single VNF instance carries the aggregated traffic of all the RAN slice subnets. Sharing gNB components between RAN slice subnets could optimize the trade-off between customization, isolation and resource utilization. In this article, we shed light on the key aspects in the Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP)/NFV standards for sharing gNB components. First, we identify four possible scenarios for sharing gNB components. Then, we analyze the impact of sharing on the customization level of each RAN slice subnet. Later, we determine the main factors that enable isolation between RAN slice subnets. Finally, we propose a 3GPP/NFV-based description model to define the lifecycle management of shared gNB components.}, keywords={3GPP;Computer architecture;Ultra reliable low latency communication;Protocols;Next generation networking;Network function virtualization;3GPP;NFV;RAN slicing;sharing gNB components;description model}, doi={10.1109/CSCN.2019.8931318}, ISSN={2644-3252}, month={October}, project={5gcity|artemis}, pdf={https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/68197}
}
close
-
Performance of LoRaWAN networks in outdoor scenarios
The Eighteenth International Conference on Networks (ICN 2019), pp. 1-6, mar 2019.
"Performance of LoRaWAN networks in outdoor scenarios", Pablo Romero-Diaz, Laura Garcia, Sandra Sendra, Jorge Navarro-Ortiz, "The Eighteenth International Conference on Networks (ICN 2019)", ISBN 9781612086958, pp. 1-6, 2019
close
@Inproceedings{romerodiazperformance2019,
title = {Performance of {LoRaWAN} networks in outdoor scenarios},
booktitle={The Eighteenth International Conference on Networks (ICN 2019)},
isbn = {9781612086958},
url = {http://www.thinkmind.org/index.php?view=article&articleid=icn_2019_1_10_30028},
urldate = {2021-03-22},
author = {Romero-Diaz, Pablo and Garcia, Laura and Sendra, Sandra and Navarro-Ortiz, Jorge},
month = mar,
year = {2019},
pages = {1-6},
project = {5gcity}
}
close
-
Improving hardware security for LoRaWAN
2019 IEEE Conference on Standards for Communications and Networking (CSCN), pp. 1-6, 2019, DOI: 10.1109/CSCN.2019.8931397.
"Improving hardware security for LoRaWAN", J. Navarro-Ortiz, N. Chinchilla-Romero, J. J. Ramos-Munoz, P. Munoz-Luengo, "2019 IEEE Conference on Standards for Communications and Networking (CSCN)", pp. 1-6, 2019. DOI: 10.1109/CSCN.2019.8931397
close
@Inproceedings{8931397, author={J. {Navarro-Ortiz} and N. {Chinchilla-Romero} and J. J. {Ramos-Munoz} and P. {Munoz-Luengo}}, booktitle={2019 IEEE Conference on Standards for Communications and Networking (CSCN)}, title={Improving hardware security for LoRaWAN}, year={2019}, volume={}, number={}, pages={1-6}, doi={10.1109/CSCN.2019.8931397}, project="5gcity"}
close
-
A Queuing Based Dynamic Auto Scaling Algorithm for the LTE EPC Control Plane
2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), pp. 1-7, Dec 2018, DOI: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2018.8648023.
"A Queuing Based Dynamic Auto Scaling Algorithm for the LTE EPC Control Plane", J. Prados-Garzon, A. Laghrissi, M. Bagaa, T. Taleb, "2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM)", pp. 1-7, 2018. DOI: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2018.8648023
close
The network softwarization paradigm, enabled by Network Function Virtualization (NFV), facilitates the automation of management operations and orchestration of future networks, thus reducing their operational expenditures. The envisioned management practices include the introduction of automation in the scaling of network services. This may enable operators to handle workload fluctuations, to keep the desired performance, with great agility and reduced costs. This procedure introduces a non-negligible delay in allocating or releasing virtual resources. Therefore, waiting until the system is overloaded or underutilized so as to scale resources up or down could negatively impact the users' Quality of Experience, or lead to inefficient resource utilization. In this vein, this paper proposes a novel and agile Dynamic Auto Scaling Algorithm for the Control Plane (CP) of the Long Term Evolution' (LTE) virtualized Evolved Packet Core (vEPC). The resources dimensioning stage of the algorithm is based on an original queuing model for the CP. To model the CP, we use an open network of G/G/m queues. We also provide expressions to derive the steady state transition probabilities of the queuing network. Finally, we validate the proper operation of our solution using accurate simulation tools.
close
@INPROCEEDINGS{8648023, author={J. {Prados-Garzon} and A. {Laghrissi} and M. {Bagaa} and T. {Taleb}}, booktitle={2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM)}, title={A Queuing Based Dynamic Auto Scaling Algorithm for the LTE EPC Control Plane}, year={2018}, volume={}, number={}, pages={1-7}, abstract={The network softwarization paradigm, enabled by Network Function Virtualization (NFV), facilitates the automation of management operations and orchestration of future networks, thus reducing their operational expenditures. The envisioned management practices include the introduction of automation in the scaling of network services. This may enable operators to handle workload fluctuations, to keep the desired performance, with great agility and reduced costs. This procedure introduces a non-negligible delay in allocating or releasing virtual resources. Therefore, waiting until the system is overloaded or underutilized so as to scale resources up or down could negatively impact the users' Quality of Experience, or lead to inefficient resource utilization. In this vein, this paper proposes a novel and agile Dynamic Auto Scaling Algorithm for the Control Plane (CP) of the Long Term Evolution' (LTE) virtualized Evolved Packet Core (vEPC). The resources dimensioning stage of the algorithm is based on an original queuing model for the CP. To model the CP, we use an open network of G/G/m queues. We also provide expressions to derive the steady state transition probabilities of the queuing network. Finally, we validate the proper operation of our solution using accurate simulation tools.}, keywords={Long Term Evolution;Queueing analysis;Heuristic algorithms;Servers;Analytical models;Delays;Adaptation models}, doi={10.1109/GLOCOM.2018.8648023}, ISSN={2576-6813}, month={Dec}, project={5gcity}
}
close
-
Energy and Delay Aware Physical Collision Avoidance in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles
2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), pp. 1-7, Dec 2018, DOI: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2018.8647223.
"Energy and Delay Aware Physical Collision Avoidance in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles", S. Ouahouah, J. Prados-Garzon, T. Taleb, C. Benzaid, "2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM)", pp. 1-7, 2018. DOI: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2018.8647223
close
Several solutions have been proposed in the literature to address the Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) collision avoidance problem. Most of these solutions consider that the ground controller system (GCS) determines the path of a UAV before starting a particular mission at hand. Furthermore, these solutions expect the occurrence of collisions based only on the GPS localization of UAVs as well as via object-detecting sensors placed on board UAVs. The sensors' sensitivity to environmental disturbances and the UAVs' influence on their accuracy impact negatively the efficiency of these solutions. In this vein, this paper proposes a new energy- and delay-aware physical collision avoidance solution for UAVs. The solution is dubbed EDCUAV. The primary goal of EDC-UAV is to build in-flight safe UAVs trajectories while minimizing the energy consumption and response time. We assume that each UAV is equipped with a global positioning system (GPS) sensor to identify its position. Moreover, we take into account the margin error of the GPS to provide the position of a given UAV. The location of each UAV is gathered by a cluster head, which is the UAV that has either the highest autonomy or the greatest computational capacity. The cluster head runs the EDC-UAV algorithm to control the rest of the UAVs, thus guaranteeing a collision free mission and minimizing the energy consumption to achieve different purposes. The proper operation of our solution is validated through simulations. The obtained results demonstrate the efficiency of EDC-UAV in achieving its design goals.
close
@INPROCEEDINGS{8647223, author={S. {Ouahouah} and J. {Prados-Garzon} and T. {Taleb} and C. {Benzaid}}, booktitle={2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM)}, title={Energy and Delay Aware Physical Collision Avoidance in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles}, year={2018}, volume={}, number={}, pages={1-7}, abstract={Several solutions have been proposed in the literature to address the Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) collision avoidance problem. Most of these solutions consider that the ground controller system (GCS) determines the path of a UAV before starting a particular mission at hand. Furthermore, these solutions expect the occurrence of collisions based only on the GPS localization of UAVs as well as via object-detecting sensors placed on board UAVs. The sensors' sensitivity to environmental disturbances and the UAVs' influence on their accuracy impact negatively the efficiency of these solutions. In this vein, this paper proposes a new energy- and delay-aware physical collision avoidance solution for UAVs. The solution is dubbed EDCUAV. The primary goal of EDC-UAV is to build in-flight safe UAVs trajectories while minimizing the energy consumption and response time. We assume that each UAV is equipped with a global positioning system (GPS) sensor to identify its position. Moreover, we take into account the margin error of the GPS to provide the position of a given UAV. The location of each UAV is gathered by a cluster head, which is the UAV that has either the highest autonomy or the greatest computational capacity. The cluster head runs the EDC-UAV algorithm to control the rest of the UAVs, thus guaranteeing a collision free mission and minimizing the energy consumption to achieve different purposes. The proper operation of our solution is validated through simulations. The obtained results demonstrate the efficiency of EDC-UAV in achieving its design goals.}, keywords={Global Positioning System;Unmanned aerial vehicles;Collision avoidance;Sensors;Trajectory;Optimization;Energy consumption}, doi={10.1109/GLOCOM.2018.8647223}, ISSN={2576-6813}, month={Dec}, project={5gcity}
}
close
-
The Creation Phase in Network Slicing: From a Service Order to an Operative Network Slice
2018 European Conference on Networks and Communications (EuCNC), pp. 1-36, June 2018, DOI: 10.1109/EuCNC.2018.8443255.
"The Creation Phase in Network Slicing: From a Service Order to an Operative Network Slice", J. Ordonez-Lucena, O. Adamuz-Hinojosa, P. Ameigeiras, P. Munoz, J. J. Ramos-Munoz, J. F. Chavarria, D. Lopez, "2018 European Conference on Networks and Communications (EuCNC)", pp. 1-36, 2018. DOI: 10.1109/EuCNC.2018.8443255
close
Network slicing is considered a key mechanism to serve the multitude of tenants (e.g. vertical industries) targeted by forthcoming 5G systems in a flexible and cost-efficient manner. In this paper, we present a SDN/NFV architecture with multi-tenancy support. This architecture enables a network slice provider to deploy network slice instances for multiple tenants on-the-fly, and simultaneously provision them with isolation guarantees. Following the Network Slice as-a-Service delivery model, a tenant may access a Service Catalog, selecting the slice that best fits its needs and ordering its deployment. This work provides a detailed view on the stages that a network slice provider must follow to deploy the ordered network slice instance, accommodating it into a multi-domain infrastructure, and putting it operative for tenant's consumption. These stages address critical issues identified in the literature, including (i) the mapping from high-level service requirements to network functions and infrastructure requirements, (ii) the admission control, and (iii) the specific information a network slice descriptor should have. With the proposed architecture and the recommended set of stages, network slice providers can deploy (and later operate) slice instances with great agility, flexibility, and full automation.
close
@INPROCEEDINGS{8443255,
author={J. {Ordonez-Lucena} and O. {Adamuz-Hinojosa} and P. {Ameigeiras} and P. {Munoz} and J. J. {Ramos-Munoz} and J. F. {Chavarria} and D. {Lopez}},
booktitle={2018 European Conference on Networks and Communications (EuCNC)},
title={The Creation Phase in Network Slicing: From a Service Order to an Operative Network Slice},
year={2018},
volume={},
number={},
pages={1-36},
abstract={Network slicing is considered a key mechanism to serve the multitude of tenants (e.g. vertical industries) targeted by forthcoming 5G systems in a flexible and cost-efficient manner. In this paper, we present a SDN/NFV architecture with multi-tenancy support. This architecture enables a network slice provider to deploy network slice instances for multiple tenants on-the-fly, and simultaneously provision them with isolation guarantees. Following the Network Slice as-a-Service delivery model, a tenant may access a Service Catalog, selecting the slice that best fits its needs and ordering its deployment. This work provides a detailed view on the stages that a network slice provider must follow to deploy the ordered network slice instance, accommodating it into a multi-domain infrastructure, and putting it operative for tenant's consumption. These stages address critical issues identified in the literature, including (i) the mapping from high-level service requirements to network functions and infrastructure requirements, (ii) the admission control, and (iii) the specific information a network slice descriptor should have. With the proposed architecture and the recommended set of stages, network slice providers can deploy (and later operate) slice instances with great agility, flexibility, and full automation.},
keywords={5G mobile communication;quality of service;software defined networking;telecommunication congestion control;virtualisation;admission control;multidomain infrastructure;service catalog;network slice as-a-service delivery;SDN-NFV architecture;5G systems;operative network slice;network slice descriptor;ordered network slice instance;network slice provider;Network slicing;Computer architecture;Business;Europe;Wide area networks;Containers;Industries;Network Slicing;SDN;NFV;Service Catalog;Slice Instance Creation},
doi={10.1109/EuCNC.2018.8443255},
ISSN={2575-4912},
month={June}, project={5gcity}, pdf={https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/68204}
}
close
-
WiMuNet's research on 5G and QoE
IV Workshop on QoE, QoS on Multimedia Communications (QQCM'18), 2018.
CITE
BibTeX
"WiMuNet's research on 5G and QoE", J. Prados-Garzon, P. Andres-Maldonado, P. Romero-Diaz, J. Navarro-Ortiz, J. J. Ramos-Munoz, P. Ameigeiras, P. Munoz-Luengo, S. Sendra, J. M. Lopez-Soler, "IV Workshop on QoE, QoS on Multimedia Communications (QQCM'18)", 2018
close
@Inproceedings{jpradosqqcm18, author={J. {Prados-Garzon} and P. {Andres-Maldonado} and P. {Romero-Diaz} and J. {Navarro-Ortiz} and J. J. {Ramos-Munoz} and P. {Ameigeiras} and P. {Munoz-Luengo} and S. {Sendra} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler}}, booktitle={IV Workshop on QoE, QoS on Multimedia Communications (QQCM'18)}, title={WiMuNet's research on 5G and QoE}, year={2018}, project={5gcity}}
close
-
An architecture for the 5G control plane based on SDN and data distribution service
2018 Fifth International Conference on Software Defined Systems (SDS), pp. 105-111, 2018, DOI: 10.1109/SDS.2018.8370430.
"An architecture for the 5G control plane based on SDN and data distribution service", A. Llorens-Carrodeguas, C. Cervello-Pastor, I. Leyva-Pupo, J. M. Lopez-Soler, J. Navarro-Ortiz, J. A. Exposito-Arenas, "2018 Fifth International Conference on Software Defined Systems (SDS)", pp. 105-111, 2018. DOI: 10.1109/SDS.2018.8370430
close
@Inproceedings{8370430, author={A. {Llorens-Carrodeguas} and C. {Cervello-Pastor} and I. {Leyva-Pupo} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler} and J. {Navarro-Ortiz} and J. A. {Exposito-Arenas}}, booktitle={2018 Fifth International Conference on Software Defined Systems (SDS)}, title={An architecture for the 5G control plane based on SDN and data distribution service}, year={2018}, volume={}, number={}, pages={105-111}, doi={10.1109/SDS.2018.8370430}, project={5gcity}}
close
-
Performance of LoRaWAN on a Highway Scenario
XXXIII Simposium Nacional de la Union Cientifica Internacional de Radio (URSI 2018), 2018.
"Performance of LoRaWAN on a Highway Scenario", P. Romero-Diaz, J. Navarro-Ortiz, S. Sendra, J. J. Ramos-Munoz, "XXXIII Simposium Nacional de la Union Cientifica Internacional de Radio (URSI 2018)", 2018
close
@Inproceedings{promeroursi18, author={P. {Romero-Diaz} and J. {Navarro-Ortiz} and S. {Sendra} and J. J. {Ramos-Munoz}}, booktitle={XXXIII Simposium Nacional de la Union Cientifica Internacional de Radio (URSI 2018)}, title={Performance of LoRaWAN on a Highway Scenario}, year={2018}, url={http://wpd.ugr.es/~jorgenavarro/publications/preprint_ursi2018_lorawan-performance-highway.pdf}, project="5gcity"}
close
-
The Roll of Data Distribution Service in Failure-aware SDN Controllers
XXXIII Simposium Nacional de la Union Cientifica Internacional de Radio (URSI 2018), 2018.
"The Roll of Data Distribution Service in Failure-aware SDN Controllers", A. Llorens-Carrodeaguas, C. Cervello-Pastor, I. Leyva-Pupo, J. M. Lopez-Soler, J. Navarro-Ortiz, "XXXIII Simposium Nacional de la Union Cientifica Internacional de Radio (URSI 2018)", 2018
close
@Inproceedings{allorensursi18, author={A. {Llorens-Carrodeaguas} and C. {Cervello-Pastor} and I. {Leyva-Pupo} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler} and J. {Navarro-Ortiz}}, booktitle={XXXIII Simposium Nacional de la Union Cientifica Internacional de Radio (URSI 2018)}, title={The Roll of Data Distribution Service in Failure-aware SDN Controllers}, year={2018}, url={http://wpd.ugr.es/~jorgenavarro/publications/preprint_dds_sdn_controllers.pdf}, project={5gcity}, pdf={https://upcommons.upc.edu/handle/2117/126845}}
close
-
Smart Infant Incubator Based on LoRa Networks
2018 IEEE/ACS 15th International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA), pp. 1-6, 2018, DOI: 10.1109/AICCSA.2018.8612863.
"Smart Infant Incubator Based on LoRa Networks", S. Sendra, P. Romero-Diaz, J. Navarro-Ortiz, J. Lloret, "2018 IEEE/ACS 15th International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA)", pp. 1-6, 2018. DOI: 10.1109/AICCSA.2018.8612863
close
@Inproceedings{8612863, author={S. {Sendra} and P. {Romero-Diaz} and J. {Navarro-Ortiz} and J. {Lloret}}, booktitle={2018 IEEE/ACS 15th International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA)}, title={Smart Infant Incubator Based on LoRa Networks}, year={2018}, volume={}, number={}, pages={1-6}, doi={10.1109/AICCSA.2018.8612863}, project={5gcity}}
close
-
Red SDN para el control de un aula energeticamente eficiente para la elaboracion de practicas reales a distancia
XIII Jornadas de Ingenieria Telematica - JITEL2017, October 2017.
"Red SDN para el control de un aula energeticamente eficiente para la elaboracion de practicas reales a distancia", Marina Terron-Camero, Sandra Sendra, Jorge Navarro-Ortiz, Jaime Lloret, "XIII Jornadas de Ingenieria Telematica - JITEL2017", 2017
close
@Inproceedings{terroncamerored2017,
title = {Red {SDN} para el control de un aula energeticamente eficiente para la elaboracion de practicas reales a distancia},
copyright = {Authors who submit to this conference agree to the following terms: a) Authors retain copyright over their work, while allowing the conference to place this unpublished work under a Creative Commons License , which allows others to freely access, use, and share the work, with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and its initial presentation at this conference. b) Authors are able to waive the terms of the CC license and enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution and subsequent publication of this work (e.g., publish a revised version in a journal, post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial presentation at this conference. c) In addition, authors are encouraged to post and share their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) at any point before and after the conference.},
url = {http://ocs.editorial.upv.es/index.php/JITEL/JITEL2017/paper/view/6613},
language = {es},
urldate = {2021-03-22},
booktitle = {{XIII} {Jornadas} de {Ingenieria} {Telematica} - {JITEL2017}},
author = {Terron-Camero, Marina and Sendra, Sandra and Navarro-Ortiz, Jorge and Lloret, Jaime},
month = October,
year = {2017},
project = {5gcity},
pdf = {https://riunet.upv.es/handle/10251/102657}
}
close
-
Implementacion de mecanismos de mitigacion de tormentas de broadcast en redes de area local mediante Redes Definidas por Software
XIII Jornadas de Ingenieria Telematica - JITEL2017, October 2017.
"Implementacion de mecanismos de mitigacion de tormentas de broadcast en redes de area local mediante Redes Definidas por Software", Barbara-Valera Muros, Jonathan Prados-Garzon, Juan J. Ramos-Munoz, Jorge Navarro-Ortiz, "XIII Jornadas de Ingenieria Telematica - JITEL2017", 2017
close
@Inproceedings{murosimplementacion2017,
title = {Implementacion de mecanismos de mitigacion de tormentas de broadcast en redes de area local mediante {Redes} {Definidas} por {Software}},
copyright = {Authors who submit to this conference agree to the following terms: a) Authors retain copyright over their work, while allowing the conference to place this unpublished work under a Creative Commons License , which allows others to freely access, use, and share the work, with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and its initial presentation at this conference. b) Authors are able to waive the terms of the CC license and enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution and subsequent publication of this work (e.g., publish a revised version in a journal, post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial presentation at this conference. c) In addition, authors are encouraged to post and share their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) at any point before and after the conference.},
url = {http://ocs.editorial.upv.es/index.php/JITEL/JITEL2017/paper/view/6585},
language = {es},
urldate = {2021-03-22},
booktitle = {{XIII} {Jornadas} de {Ingenieria} {Telematica} - {JITEL2017}},
author = {Muros, Barbara-Valera and Prados-Garzon, Jonathan and Ramos-Munoz, Juan J. and Navarro-Ortiz, Jorge},
month = October,
year = {2017},
project = {5gcity},
pdf={https://riunet.upv.es/handle/10251/101927}
}
close
-
Capacity self-planning in Small Cell multi-tenant 5G Networks
2017 IFIP/IEEE Symposium on Integrated Network and Service Management (IM), pp. 1109-1114, May 2017, DOI: 10.23919/INM.2017.7987449.
"Capacity self-planning in Small Cell multi-tenant 5G Networks", P. Munoz, O. Sallent, J. Perez-Romero, "2017 IFIP/IEEE Symposium on Integrated Network and Service Management (IM)", pp. 1109-1114, 2017. DOI: 10.23919/INM.2017.7987449
close
Multi-tenancy allows diverse agents sharing the infrastructure in the 5th generation of mobile networks. Such a feature calls for more automated and faster planning procedures in order to adapt the network capacity to the varying traffic demand. To achieve these goals, Small Cells offer network providers more flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solutions compared to macrocell deployments. This paper proposes a novel framework for cell planning in multi-tenant Small Cell networks. In this framework, the tenant's contracted capacity is translated to a set of detailed planning specifications over time and space domains in order to efficiently update the network infrastructure and configuration. Based on this, an algorithm is proposed that considers different actions such as adding/removing channels and adding or relocating small cells. The proposed approach is evaluated considering the deployment of a new tenant, where different sets of planning specifications are tested.
close
@INPROCEEDINGS{7987449,
author={P. {Munoz} and O. {Sallent} and J. {Perez-Romero}},
booktitle={2017 IFIP/IEEE Symposium on Integrated Network and Service Management (IM)},
title={Capacity self-planning in Small Cell multi-tenant 5G Networks},
year={2017},
volume={},
number={},
pages={1109-1114},
abstract={Multi-tenancy allows diverse agents sharing the infrastructure in the 5th generation of mobile networks. Such a feature calls for more automated and faster planning procedures in order to adapt the network capacity to the varying traffic demand. To achieve these goals, Small Cells offer network providers more flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solutions compared to macrocell deployments. This paper proposes a novel framework for cell planning in multi-tenant Small Cell networks. In this framework, the tenant's contracted capacity is translated to a set of detailed planning specifications over time and space domains in order to efficiently update the network infrastructure and configuration. Based on this, an algorithm is proposed that considers different actions such as adding/removing channels and adding or relocating small cells. The proposed approach is evaluated considering the deployment of a new tenant, where different sets of planning specifications are tested.},
keywords={5G mobile communication;cellular radio;channel capacity;telecommunication network planning;telecommunication traffic;capacity self-planning;small cell multi-tenant 5G networks;5th generation mobile networks;network capacity;traffic demand;network providers;Planning;Bandwidth;Capacity planning;Computer architecture;5G mobile communication;Measurement;Mobile computing;Capacity planning;dimensioning;multi-tenancy;Small Cells;5G networks;SON},
doi={10.23919/INM.2017.7987449},
ISSN={},
month={May},
project={related5gcity},
pdf={https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/68229}
}
close
-
Analytical modeling for Virtualized Network Functions
2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), pp. 979-985, May 2017, DOI: 10.1109/ICCW.2017.7962786.
"Analytical modeling for Virtualized Network Functions", J. Prados-Garzon, P. Ameigeiras, J. J. Ramos-Munoz, P. Andres-Maldonado, J. M. Lopez-Soler, "2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops)", pp. 979-985, 2017. DOI: 10.1109/ICCW.2017.7962786
close
Network Function Virtualization (NFV) is considered one of the key technologies for the 5G mobile networks. In NFV, network functions are implemented in software components denominated Virtual Network Functions (VNFs) running on commodity hardware. In this paper, we propose an analytical model based on an open queuing network of G/G/m queues to model VNFs with several components, and chains of VNFs. Our model is flexible and generic enough to capture the behavior of such systems. We validate our model by simulation. Specifically, we validate it for an LTE virtualized Mobility Management Entity with a three-tiered architecture use case. We also compare our model with the estate of the art, in terms of computational complexity and estimation error. The results show that our model has a computational complexity similar to the method for analyzing Jackson's networks. Additionally, our model exhibits an estimation error, measured as the relative error for the estimation of the mean response time, approximately equal to 10%, whereas for the considered baseline systems it ranges roughly from 60% to 90%.
close
@INPROCEEDINGS{7962786, author={J. {Prados-Garzon} and P. {Ameigeiras} and J. J. {Ramos-Munoz} and P. {Andres-Maldonado} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler}}, booktitle={2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops)}, title={Analytical modeling for Virtualized Network Functions}, year={2017}, volume={}, number={}, pages={979-985}, abstract={Network Function Virtualization (NFV) is considered one of the key technologies for the 5G mobile networks. In NFV, network functions are implemented in software components denominated Virtual Network Functions (VNFs) running on commodity hardware. In this paper, we propose an analytical model based on an open queuing network of G/G/m queues to model VNFs with several components, and chains of VNFs. Our model is flexible and generic enough to capture the behavior of such systems. We validate our model by simulation. Specifically, we validate it for an LTE virtualized Mobility Management Entity with a three-tiered architecture use case. We also compare our model with the estate of the art, in terms of computational complexity and estimation error. The results show that our model has a computational complexity similar to the method for analyzing Jackson's networks. Additionally, our model exhibits an estimation error, measured as the relative error for the estimation of the mean response time, approximately equal to 10%, whereas for the considered baseline systems it ranges roughly from 60% to 90%.}, keywords={Computational modeling;Analytical models;Iron;5G mobile communication;Computer architecture;Time factors;Queueing analysis;5G;NFV;VNF;analytical model;queuing model}, doi={10.1109/ICCW.2017.7962786}, ISSN={2474-9133}, month={May}, project={5gcity}
}
close
-
Optimized LTE data transmission procedures for IoT: Device side energy consumption analysis
2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), pp. 540-545, May 2017, DOI: 10.1109/ICCW.2017.7962714.
"Optimized LTE data transmission procedures for IoT: Device side energy consumption analysis", P. Andres-Maldonado, P. Ameigeiras, J. Prados-Garzon, J. J. Ramos-Munoz, J. M. Lopez-Soler, "2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops)", pp. 540-545, 2017. DOI: 10.1109/ICCW.2017.7962714
close
The efficient deployment of Internet of Things (IoT) over cellular networks, such as Long Term Evolution (LTE) or the next generation 5G, entails several challenges. For massive IoT, reducing the energy consumption on the device side becomes essential. One of the main characteristics of massive IoT is small data transmissions. To improve the support of them, the 3GPP has included two novel optimizations in LTE: one of them based on the Control Plane (CP), and the other on the User Plane (UP). In this paper, we analyze the average energy consumption per data packet using these two optimizations compared to conventional LTE Service Request procedure. We propose an analytical model to calculate the energy consumption for each procedure based on a Markov chain. In the considered scenario, for large and small Inter-Arrival Times (IATs), the results of the three procedures are similar. While for medium IATs CP reduces the energy consumption per packet up to 87% due to its connection release optimization.
close
@INPROCEEDINGS{7962714, author={P. {Andres-Maldonado} and P. {Ameigeiras} and J. {Prados-Garzon} and J. J. {Ramos-Munoz} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler}}, booktitle={2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops)}, title={Optimized LTE data transmission procedures for IoT: Device side energy consumption analysis}, year={2017}, volume={}, number={}, pages={540-545}, abstract={The efficient deployment of Internet of Things (IoT) over cellular networks, such as Long Term Evolution (LTE) or the next generation 5G, entails several challenges. For massive IoT, reducing the energy consumption on the device side becomes essential. One of the main characteristics of massive IoT is small data transmissions. To improve the support of them, the 3GPP has included two novel optimizations in LTE: one of them based on the Control Plane (CP), and the other on the User Plane (UP). In this paper, we analyze the average energy consumption per data packet using these two optimizations compared to conventional LTE Service Request procedure. We propose an analytical model to calculate the energy consumption for each procedure based on a Markov chain. In the considered scenario, for large and small Inter-Arrival Times (IATs), the results of the three procedures are similar. While for medium IATs CP reduces the energy consumption per packet up to 87% due to its connection release optimization.}, keywords={Long Term Evolution;Energy consumption;Optimization;Data communication;3GPP;Context;Security}, doi={10.1109/ICCW.2017.7962714}, ISSN={2474-9133}, month={May}, project={5gcity}, pdf={https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/68238}
}
close
-
Diseno y evaluacion de un servicio OpenFlow de provision de Calidad de Experiencia sobre Mininet
XIII Jornadas de Ingenieria Telematica (JITEL 2017), 2017.
"Diseno y evaluacion de un servicio OpenFlow de provision de Calidad de Experiencia sobre Mininet", Cristian Prieto Sanchez, P. Maldonado, Jonathan Prados Garzon, J. Ramos-Munoz, "XIII Jornadas de Ingenieria Telematica (JITEL 2017)", 2017
close
@inproceedings{Snchez2017DiseoYE,
title={Diseno y evaluacion de un servicio OpenFlow de provision de Calidad de Experiencia sobre Mininet},
booktitle={XIII Jornadas de Ingenieria Telematica (JITEL 2017)},
author={Cristian Prieto Sanchez and P. Maldonado and Jonathan Prados Garzon and J. Ramos-Munoz},
year={2017}, project={5gcity}, pdf={https://riunet.upv.es/handle/10251/101930}
}
close
Sharing gNB components in RAN slicing: A perspective from 3GPP/NFV standards2019 IEEE Conference on Standards for Communications and Networking (CSCN), pp. 1-7, October 2019, DOI: 10.1109/CSCN.2019.8931318.
"Sharing gNB components in RAN slicing: A perspective from 3GPP/NFV standards", O. Adamuz-Hinojosa, P. Munoz, P. Ameigeiras, J. M. Lopez-Soler, "2019 IEEE Conference on Standards for Communications and Networking (CSCN)", pp. 1-7, 2019. DOI: 10.1109/CSCN.2019.8931318close
To implement the next Generation NodeBs (gNBs) that are present in every Radio Access Network (RAN) slice subnet, Network Function Virtualization (NFV) enables the deployment of some of the gNB components as Virtual Networks Functions (VNFs). Deploying individual VNF instances for these components could guarantee the customization of each RAN slice subnet. However, due to the multiplicity of VNFs, the required amount of virtual resources will be greater compared to the case where a single VNF instance carries the aggregated traffic of all the RAN slice subnets. Sharing gNB components between RAN slice subnets could optimize the trade-off between customization, isolation and resource utilization. In this article, we shed light on the key aspects in the Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP)/NFV standards for sharing gNB components. First, we identify four possible scenarios for sharing gNB components. Then, we analyze the impact of sharing on the customization level of each RAN slice subnet. Later, we determine the main factors that enable isolation between RAN slice subnets. Finally, we propose a 3GPP/NFV-based description model to define the lifecycle management of shared gNB components.close
@INPROCEEDINGS{8931318, author={O. {Adamuz-Hinojosa} and P. {Munoz} and P. {Ameigeiras} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler}}, booktitle={2019 IEEE Conference on Standards for Communications and Networking (CSCN)}, title={Sharing gNB components in RAN slicing: A perspective from 3GPP/NFV standards}, year={2019}, volume={}, number={}, pages={1-7}, abstract={To implement the next Generation NodeBs (gNBs) that are present in every Radio Access Network (RAN) slice subnet, Network Function Virtualization (NFV) enables the deployment of some of the gNB components as Virtual Networks Functions (VNFs). Deploying individual VNF instances for these components could guarantee the customization of each RAN slice subnet. However, due to the multiplicity of VNFs, the required amount of virtual resources will be greater compared to the case where a single VNF instance carries the aggregated traffic of all the RAN slice subnets. Sharing gNB components between RAN slice subnets could optimize the trade-off between customization, isolation and resource utilization. In this article, we shed light on the key aspects in the Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP)/NFV standards for sharing gNB components. First, we identify four possible scenarios for sharing gNB components. Then, we analyze the impact of sharing on the customization level of each RAN slice subnet. Later, we determine the main factors that enable isolation between RAN slice subnets. Finally, we propose a 3GPP/NFV-based description model to define the lifecycle management of shared gNB components.}, keywords={3GPP;Computer architecture;Ultra reliable low latency communication;Protocols;Next generation networking;Network function virtualization;3GPP;NFV;RAN slicing;sharing gNB components;description model}, doi={10.1109/CSCN.2019.8931318}, ISSN={2644-3252}, month={October}, project={5gcity|artemis}, pdf={https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/68197}
}
close
Performance of LoRaWAN networks in outdoor scenariosThe Eighteenth International Conference on Networks (ICN 2019), pp. 1-6, mar 2019.
"Performance of LoRaWAN networks in outdoor scenarios", Pablo Romero-Diaz, Laura Garcia, Sandra Sendra, Jorge Navarro-Ortiz, "The Eighteenth International Conference on Networks (ICN 2019)", ISBN 9781612086958, pp. 1-6, 2019close
@Inproceedings{romerodiazperformance2019,
title = {Performance of {LoRaWAN} networks in outdoor scenarios},
booktitle={The Eighteenth International Conference on Networks (ICN 2019)},
isbn = {9781612086958},
url = {http://www.thinkmind.org/index.php?view=article&articleid=icn_2019_1_10_30028},
urldate = {2021-03-22},
author = {Romero-Diaz, Pablo and Garcia, Laura and Sendra, Sandra and Navarro-Ortiz, Jorge},
month = mar,
year = {2019},
pages = {1-6},
project = {5gcity}
}
close
Improving hardware security for LoRaWAN2019 IEEE Conference on Standards for Communications and Networking (CSCN), pp. 1-6, 2019, DOI: 10.1109/CSCN.2019.8931397.
"Improving hardware security for LoRaWAN", J. Navarro-Ortiz, N. Chinchilla-Romero, J. J. Ramos-Munoz, P. Munoz-Luengo, "2019 IEEE Conference on Standards for Communications and Networking (CSCN)", pp. 1-6, 2019. DOI: 10.1109/CSCN.2019.8931397close
@Inproceedings{8931397, author={J. {Navarro-Ortiz} and N. {Chinchilla-Romero} and J. J. {Ramos-Munoz} and P. {Munoz-Luengo}}, booktitle={2019 IEEE Conference on Standards for Communications and Networking (CSCN)}, title={Improving hardware security for LoRaWAN}, year={2019}, volume={}, number={}, pages={1-6}, doi={10.1109/CSCN.2019.8931397}, project="5gcity"}
close
A Queuing Based Dynamic Auto Scaling Algorithm for the LTE EPC Control Plane2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), pp. 1-7, Dec 2018, DOI: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2018.8648023.
"A Queuing Based Dynamic Auto Scaling Algorithm for the LTE EPC Control Plane", J. Prados-Garzon, A. Laghrissi, M. Bagaa, T. Taleb, "2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM)", pp. 1-7, 2018. DOI: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2018.8648023close
The network softwarization paradigm, enabled by Network Function Virtualization (NFV), facilitates the automation of management operations and orchestration of future networks, thus reducing their operational expenditures. The envisioned management practices include the introduction of automation in the scaling of network services. This may enable operators to handle workload fluctuations, to keep the desired performance, with great agility and reduced costs. This procedure introduces a non-negligible delay in allocating or releasing virtual resources. Therefore, waiting until the system is overloaded or underutilized so as to scale resources up or down could negatively impact the users' Quality of Experience, or lead to inefficient resource utilization. In this vein, this paper proposes a novel and agile Dynamic Auto Scaling Algorithm for the Control Plane (CP) of the Long Term Evolution' (LTE) virtualized Evolved Packet Core (vEPC). The resources dimensioning stage of the algorithm is based on an original queuing model for the CP. To model the CP, we use an open network of G/G/m queues. We also provide expressions to derive the steady state transition probabilities of the queuing network. Finally, we validate the proper operation of our solution using accurate simulation tools.close
@INPROCEEDINGS{8648023, author={J. {Prados-Garzon} and A. {Laghrissi} and M. {Bagaa} and T. {Taleb}}, booktitle={2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM)}, title={A Queuing Based Dynamic Auto Scaling Algorithm for the LTE EPC Control Plane}, year={2018}, volume={}, number={}, pages={1-7}, abstract={The network softwarization paradigm, enabled by Network Function Virtualization (NFV), facilitates the automation of management operations and orchestration of future networks, thus reducing their operational expenditures. The envisioned management practices include the introduction of automation in the scaling of network services. This may enable operators to handle workload fluctuations, to keep the desired performance, with great agility and reduced costs. This procedure introduces a non-negligible delay in allocating or releasing virtual resources. Therefore, waiting until the system is overloaded or underutilized so as to scale resources up or down could negatively impact the users' Quality of Experience, or lead to inefficient resource utilization. In this vein, this paper proposes a novel and agile Dynamic Auto Scaling Algorithm for the Control Plane (CP) of the Long Term Evolution' (LTE) virtualized Evolved Packet Core (vEPC). The resources dimensioning stage of the algorithm is based on an original queuing model for the CP. To model the CP, we use an open network of G/G/m queues. We also provide expressions to derive the steady state transition probabilities of the queuing network. Finally, we validate the proper operation of our solution using accurate simulation tools.}, keywords={Long Term Evolution;Queueing analysis;Heuristic algorithms;Servers;Analytical models;Delays;Adaptation models}, doi={10.1109/GLOCOM.2018.8648023}, ISSN={2576-6813}, month={Dec}, project={5gcity}
}
close
Energy and Delay Aware Physical Collision Avoidance in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), pp. 1-7, Dec 2018, DOI: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2018.8647223.
"Energy and Delay Aware Physical Collision Avoidance in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles", S. Ouahouah, J. Prados-Garzon, T. Taleb, C. Benzaid, "2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM)", pp. 1-7, 2018. DOI: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2018.8647223close
Several solutions have been proposed in the literature to address the Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) collision avoidance problem. Most of these solutions consider that the ground controller system (GCS) determines the path of a UAV before starting a particular mission at hand. Furthermore, these solutions expect the occurrence of collisions based only on the GPS localization of UAVs as well as via object-detecting sensors placed on board UAVs. The sensors' sensitivity to environmental disturbances and the UAVs' influence on their accuracy impact negatively the efficiency of these solutions. In this vein, this paper proposes a new energy- and delay-aware physical collision avoidance solution for UAVs. The solution is dubbed EDCUAV. The primary goal of EDC-UAV is to build in-flight safe UAVs trajectories while minimizing the energy consumption and response time. We assume that each UAV is equipped with a global positioning system (GPS) sensor to identify its position. Moreover, we take into account the margin error of the GPS to provide the position of a given UAV. The location of each UAV is gathered by a cluster head, which is the UAV that has either the highest autonomy or the greatest computational capacity. The cluster head runs the EDC-UAV algorithm to control the rest of the UAVs, thus guaranteeing a collision free mission and minimizing the energy consumption to achieve different purposes. The proper operation of our solution is validated through simulations. The obtained results demonstrate the efficiency of EDC-UAV in achieving its design goals.close
@INPROCEEDINGS{8647223, author={S. {Ouahouah} and J. {Prados-Garzon} and T. {Taleb} and C. {Benzaid}}, booktitle={2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM)}, title={Energy and Delay Aware Physical Collision Avoidance in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles}, year={2018}, volume={}, number={}, pages={1-7}, abstract={Several solutions have been proposed in the literature to address the Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) collision avoidance problem. Most of these solutions consider that the ground controller system (GCS) determines the path of a UAV before starting a particular mission at hand. Furthermore, these solutions expect the occurrence of collisions based only on the GPS localization of UAVs as well as via object-detecting sensors placed on board UAVs. The sensors' sensitivity to environmental disturbances and the UAVs' influence on their accuracy impact negatively the efficiency of these solutions. In this vein, this paper proposes a new energy- and delay-aware physical collision avoidance solution for UAVs. The solution is dubbed EDCUAV. The primary goal of EDC-UAV is to build in-flight safe UAVs trajectories while minimizing the energy consumption and response time. We assume that each UAV is equipped with a global positioning system (GPS) sensor to identify its position. Moreover, we take into account the margin error of the GPS to provide the position of a given UAV. The location of each UAV is gathered by a cluster head, which is the UAV that has either the highest autonomy or the greatest computational capacity. The cluster head runs the EDC-UAV algorithm to control the rest of the UAVs, thus guaranteeing a collision free mission and minimizing the energy consumption to achieve different purposes. The proper operation of our solution is validated through simulations. The obtained results demonstrate the efficiency of EDC-UAV in achieving its design goals.}, keywords={Global Positioning System;Unmanned aerial vehicles;Collision avoidance;Sensors;Trajectory;Optimization;Energy consumption}, doi={10.1109/GLOCOM.2018.8647223}, ISSN={2576-6813}, month={Dec}, project={5gcity}
}
close
The Creation Phase in Network Slicing: From a Service Order to an Operative Network Slice2018 European Conference on Networks and Communications (EuCNC), pp. 1-36, June 2018, DOI: 10.1109/EuCNC.2018.8443255.
"The Creation Phase in Network Slicing: From a Service Order to an Operative Network Slice", J. Ordonez-Lucena, O. Adamuz-Hinojosa, P. Ameigeiras, P. Munoz, J. J. Ramos-Munoz, J. F. Chavarria, D. Lopez, "2018 European Conference on Networks and Communications (EuCNC)", pp. 1-36, 2018. DOI: 10.1109/EuCNC.2018.8443255close
Network slicing is considered a key mechanism to serve the multitude of tenants (e.g. vertical industries) targeted by forthcoming 5G systems in a flexible and cost-efficient manner. In this paper, we present a SDN/NFV architecture with multi-tenancy support. This architecture enables a network slice provider to deploy network slice instances for multiple tenants on-the-fly, and simultaneously provision them with isolation guarantees. Following the Network Slice as-a-Service delivery model, a tenant may access a Service Catalog, selecting the slice that best fits its needs and ordering its deployment. This work provides a detailed view on the stages that a network slice provider must follow to deploy the ordered network slice instance, accommodating it into a multi-domain infrastructure, and putting it operative for tenant's consumption. These stages address critical issues identified in the literature, including (i) the mapping from high-level service requirements to network functions and infrastructure requirements, (ii) the admission control, and (iii) the specific information a network slice descriptor should have. With the proposed architecture and the recommended set of stages, network slice providers can deploy (and later operate) slice instances with great agility, flexibility, and full automation.close
@INPROCEEDINGS{8443255,
author={J. {Ordonez-Lucena} and O. {Adamuz-Hinojosa} and P. {Ameigeiras} and P. {Munoz} and J. J. {Ramos-Munoz} and J. F. {Chavarria} and D. {Lopez}},
booktitle={2018 European Conference on Networks and Communications (EuCNC)},
title={The Creation Phase in Network Slicing: From a Service Order to an Operative Network Slice},
year={2018},
volume={},
number={},
pages={1-36},
abstract={Network slicing is considered a key mechanism to serve the multitude of tenants (e.g. vertical industries) targeted by forthcoming 5G systems in a flexible and cost-efficient manner. In this paper, we present a SDN/NFV architecture with multi-tenancy support. This architecture enables a network slice provider to deploy network slice instances for multiple tenants on-the-fly, and simultaneously provision them with isolation guarantees. Following the Network Slice as-a-Service delivery model, a tenant may access a Service Catalog, selecting the slice that best fits its needs and ordering its deployment. This work provides a detailed view on the stages that a network slice provider must follow to deploy the ordered network slice instance, accommodating it into a multi-domain infrastructure, and putting it operative for tenant's consumption. These stages address critical issues identified in the literature, including (i) the mapping from high-level service requirements to network functions and infrastructure requirements, (ii) the admission control, and (iii) the specific information a network slice descriptor should have. With the proposed architecture and the recommended set of stages, network slice providers can deploy (and later operate) slice instances with great agility, flexibility, and full automation.},
keywords={5G mobile communication;quality of service;software defined networking;telecommunication congestion control;virtualisation;admission control;multidomain infrastructure;service catalog;network slice as-a-service delivery;SDN-NFV architecture;5G systems;operative network slice;network slice descriptor;ordered network slice instance;network slice provider;Network slicing;Computer architecture;Business;Europe;Wide area networks;Containers;Industries;Network Slicing;SDN;NFV;Service Catalog;Slice Instance Creation},
doi={10.1109/EuCNC.2018.8443255},
ISSN={2575-4912},
month={June}, project={5gcity}, pdf={https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/68204}
}
close
WiMuNet's research on 5G and QoEIV Workshop on QoE, QoS on Multimedia Communications (QQCM'18), 2018.
CITE
BibTeX
"WiMuNet's research on 5G and QoE", J. Prados-Garzon, P. Andres-Maldonado, P. Romero-Diaz, J. Navarro-Ortiz, J. J. Ramos-Munoz, P. Ameigeiras, P. Munoz-Luengo, S. Sendra, J. M. Lopez-Soler, "IV Workshop on QoE, QoS on Multimedia Communications (QQCM'18)", 2018close
@Inproceedings{jpradosqqcm18, author={J. {Prados-Garzon} and P. {Andres-Maldonado} and P. {Romero-Diaz} and J. {Navarro-Ortiz} and J. J. {Ramos-Munoz} and P. {Ameigeiras} and P. {Munoz-Luengo} and S. {Sendra} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler}}, booktitle={IV Workshop on QoE, QoS on Multimedia Communications (QQCM'18)}, title={WiMuNet's research on 5G and QoE}, year={2018}, project={5gcity}}
close
An architecture for the 5G control plane based on SDN and data distribution service2018 Fifth International Conference on Software Defined Systems (SDS), pp. 105-111, 2018, DOI: 10.1109/SDS.2018.8370430.
"An architecture for the 5G control plane based on SDN and data distribution service", A. Llorens-Carrodeguas, C. Cervello-Pastor, I. Leyva-Pupo, J. M. Lopez-Soler, J. Navarro-Ortiz, J. A. Exposito-Arenas, "2018 Fifth International Conference on Software Defined Systems (SDS)", pp. 105-111, 2018. DOI: 10.1109/SDS.2018.8370430close
@Inproceedings{8370430, author={A. {Llorens-Carrodeguas} and C. {Cervello-Pastor} and I. {Leyva-Pupo} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler} and J. {Navarro-Ortiz} and J. A. {Exposito-Arenas}}, booktitle={2018 Fifth International Conference on Software Defined Systems (SDS)}, title={An architecture for the 5G control plane based on SDN and data distribution service}, year={2018}, volume={}, number={}, pages={105-111}, doi={10.1109/SDS.2018.8370430}, project={5gcity}}
close
Performance of LoRaWAN on a Highway ScenarioXXXIII Simposium Nacional de la Union Cientifica Internacional de Radio (URSI 2018), 2018.
"Performance of LoRaWAN on a Highway Scenario", P. Romero-Diaz, J. Navarro-Ortiz, S. Sendra, J. J. Ramos-Munoz, "XXXIII Simposium Nacional de la Union Cientifica Internacional de Radio (URSI 2018)", 2018close
@Inproceedings{promeroursi18, author={P. {Romero-Diaz} and J. {Navarro-Ortiz} and S. {Sendra} and J. J. {Ramos-Munoz}}, booktitle={XXXIII Simposium Nacional de la Union Cientifica Internacional de Radio (URSI 2018)}, title={Performance of LoRaWAN on a Highway Scenario}, year={2018}, url={http://wpd.ugr.es/~jorgenavarro/publications/preprint_ursi2018_lorawan-performance-highway.pdf}, project="5gcity"}
close
The Roll of Data Distribution Service in Failure-aware SDN ControllersXXXIII Simposium Nacional de la Union Cientifica Internacional de Radio (URSI 2018), 2018.
"The Roll of Data Distribution Service in Failure-aware SDN Controllers", A. Llorens-Carrodeaguas, C. Cervello-Pastor, I. Leyva-Pupo, J. M. Lopez-Soler, J. Navarro-Ortiz, "XXXIII Simposium Nacional de la Union Cientifica Internacional de Radio (URSI 2018)", 2018close
@Inproceedings{allorensursi18, author={A. {Llorens-Carrodeaguas} and C. {Cervello-Pastor} and I. {Leyva-Pupo} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler} and J. {Navarro-Ortiz}}, booktitle={XXXIII Simposium Nacional de la Union Cientifica Internacional de Radio (URSI 2018)}, title={The Roll of Data Distribution Service in Failure-aware SDN Controllers}, year={2018}, url={http://wpd.ugr.es/~jorgenavarro/publications/preprint_dds_sdn_controllers.pdf}, project={5gcity}, pdf={https://upcommons.upc.edu/handle/2117/126845}}
close
Smart Infant Incubator Based on LoRa Networks2018 IEEE/ACS 15th International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA), pp. 1-6, 2018, DOI: 10.1109/AICCSA.2018.8612863.
"Smart Infant Incubator Based on LoRa Networks", S. Sendra, P. Romero-Diaz, J. Navarro-Ortiz, J. Lloret, "2018 IEEE/ACS 15th International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA)", pp. 1-6, 2018. DOI: 10.1109/AICCSA.2018.8612863close
@Inproceedings{8612863, author={S. {Sendra} and P. {Romero-Diaz} and J. {Navarro-Ortiz} and J. {Lloret}}, booktitle={2018 IEEE/ACS 15th International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA)}, title={Smart Infant Incubator Based on LoRa Networks}, year={2018}, volume={}, number={}, pages={1-6}, doi={10.1109/AICCSA.2018.8612863}, project={5gcity}}
close
Red SDN para el control de un aula energeticamente eficiente para la elaboracion de practicas reales a distanciaXIII Jornadas de Ingenieria Telematica - JITEL2017, October 2017.
"Red SDN para el control de un aula energeticamente eficiente para la elaboracion de practicas reales a distancia", Marina Terron-Camero, Sandra Sendra, Jorge Navarro-Ortiz, Jaime Lloret, "XIII Jornadas de Ingenieria Telematica - JITEL2017", 2017close
@Inproceedings{terroncamerored2017,
title = {Red {SDN} para el control de un aula energeticamente eficiente para la elaboracion de practicas reales a distancia},
copyright = {Authors who submit to this conference agree to the following terms: a) Authors retain copyright over their work, while allowing the conference to place this unpublished work under a Creative Commons License , which allows others to freely access, use, and share the work, with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and its initial presentation at this conference. b) Authors are able to waive the terms of the CC license and enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution and subsequent publication of this work (e.g., publish a revised version in a journal, post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial presentation at this conference. c) In addition, authors are encouraged to post and share their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) at any point before and after the conference.},
url = {http://ocs.editorial.upv.es/index.php/JITEL/JITEL2017/paper/view/6613},
language = {es},
urldate = {2021-03-22},
booktitle = {{XIII} {Jornadas} de {Ingenieria} {Telematica} - {JITEL2017}},
author = {Terron-Camero, Marina and Sendra, Sandra and Navarro-Ortiz, Jorge and Lloret, Jaime},
month = October,
year = {2017},
project = {5gcity},
pdf = {https://riunet.upv.es/handle/10251/102657}
}
close
Implementacion de mecanismos de mitigacion de tormentas de broadcast en redes de area local mediante Redes Definidas por SoftwareXIII Jornadas de Ingenieria Telematica - JITEL2017, October 2017.
"Implementacion de mecanismos de mitigacion de tormentas de broadcast en redes de area local mediante Redes Definidas por Software", Barbara-Valera Muros, Jonathan Prados-Garzon, Juan J. Ramos-Munoz, Jorge Navarro-Ortiz, "XIII Jornadas de Ingenieria Telematica - JITEL2017", 2017close
@Inproceedings{murosimplementacion2017,
title = {Implementacion de mecanismos de mitigacion de tormentas de broadcast en redes de area local mediante {Redes} {Definidas} por {Software}},
copyright = {Authors who submit to this conference agree to the following terms: a) Authors retain copyright over their work, while allowing the conference to place this unpublished work under a Creative Commons License , which allows others to freely access, use, and share the work, with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and its initial presentation at this conference. b) Authors are able to waive the terms of the CC license and enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution and subsequent publication of this work (e.g., publish a revised version in a journal, post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial presentation at this conference. c) In addition, authors are encouraged to post and share their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) at any point before and after the conference.},
url = {http://ocs.editorial.upv.es/index.php/JITEL/JITEL2017/paper/view/6585},
language = {es},
urldate = {2021-03-22},
booktitle = {{XIII} {Jornadas} de {Ingenieria} {Telematica} - {JITEL2017}},
author = {Muros, Barbara-Valera and Prados-Garzon, Jonathan and Ramos-Munoz, Juan J. and Navarro-Ortiz, Jorge},
month = October,
year = {2017},
project = {5gcity},
pdf={https://riunet.upv.es/handle/10251/101927}
}
close
Capacity self-planning in Small Cell multi-tenant 5G Networks2017 IFIP/IEEE Symposium on Integrated Network and Service Management (IM), pp. 1109-1114, May 2017, DOI: 10.23919/INM.2017.7987449.
"Capacity self-planning in Small Cell multi-tenant 5G Networks", P. Munoz, O. Sallent, J. Perez-Romero, "2017 IFIP/IEEE Symposium on Integrated Network and Service Management (IM)", pp. 1109-1114, 2017. DOI: 10.23919/INM.2017.7987449close
Multi-tenancy allows diverse agents sharing the infrastructure in the 5th generation of mobile networks. Such a feature calls for more automated and faster planning procedures in order to adapt the network capacity to the varying traffic demand. To achieve these goals, Small Cells offer network providers more flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solutions compared to macrocell deployments. This paper proposes a novel framework for cell planning in multi-tenant Small Cell networks. In this framework, the tenant's contracted capacity is translated to a set of detailed planning specifications over time and space domains in order to efficiently update the network infrastructure and configuration. Based on this, an algorithm is proposed that considers different actions such as adding/removing channels and adding or relocating small cells. The proposed approach is evaluated considering the deployment of a new tenant, where different sets of planning specifications are tested.close
@INPROCEEDINGS{7987449,
author={P. {Munoz} and O. {Sallent} and J. {Perez-Romero}},
booktitle={2017 IFIP/IEEE Symposium on Integrated Network and Service Management (IM)},
title={Capacity self-planning in Small Cell multi-tenant 5G Networks},
year={2017},
volume={},
number={},
pages={1109-1114},
abstract={Multi-tenancy allows diverse agents sharing the infrastructure in the 5th generation of mobile networks. Such a feature calls for more automated and faster planning procedures in order to adapt the network capacity to the varying traffic demand. To achieve these goals, Small Cells offer network providers more flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solutions compared to macrocell deployments. This paper proposes a novel framework for cell planning in multi-tenant Small Cell networks. In this framework, the tenant's contracted capacity is translated to a set of detailed planning specifications over time and space domains in order to efficiently update the network infrastructure and configuration. Based on this, an algorithm is proposed that considers different actions such as adding/removing channels and adding or relocating small cells. The proposed approach is evaluated considering the deployment of a new tenant, where different sets of planning specifications are tested.},
keywords={5G mobile communication;cellular radio;channel capacity;telecommunication network planning;telecommunication traffic;capacity self-planning;small cell multi-tenant 5G networks;5th generation mobile networks;network capacity;traffic demand;network providers;Planning;Bandwidth;Capacity planning;Computer architecture;5G mobile communication;Measurement;Mobile computing;Capacity planning;dimensioning;multi-tenancy;Small Cells;5G networks;SON},
doi={10.23919/INM.2017.7987449},
ISSN={},
month={May},
project={related5gcity},
pdf={https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/68229}
}
close
Analytical modeling for Virtualized Network Functions2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), pp. 979-985, May 2017, DOI: 10.1109/ICCW.2017.7962786.
"Analytical modeling for Virtualized Network Functions", J. Prados-Garzon, P. Ameigeiras, J. J. Ramos-Munoz, P. Andres-Maldonado, J. M. Lopez-Soler, "2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops)", pp. 979-985, 2017. DOI: 10.1109/ICCW.2017.7962786close
Network Function Virtualization (NFV) is considered one of the key technologies for the 5G mobile networks. In NFV, network functions are implemented in software components denominated Virtual Network Functions (VNFs) running on commodity hardware. In this paper, we propose an analytical model based on an open queuing network of G/G/m queues to model VNFs with several components, and chains of VNFs. Our model is flexible and generic enough to capture the behavior of such systems. We validate our model by simulation. Specifically, we validate it for an LTE virtualized Mobility Management Entity with a three-tiered architecture use case. We also compare our model with the estate of the art, in terms of computational complexity and estimation error. The results show that our model has a computational complexity similar to the method for analyzing Jackson's networks. Additionally, our model exhibits an estimation error, measured as the relative error for the estimation of the mean response time, approximately equal to 10%, whereas for the considered baseline systems it ranges roughly from 60% to 90%.close
@INPROCEEDINGS{7962786, author={J. {Prados-Garzon} and P. {Ameigeiras} and J. J. {Ramos-Munoz} and P. {Andres-Maldonado} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler}}, booktitle={2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops)}, title={Analytical modeling for Virtualized Network Functions}, year={2017}, volume={}, number={}, pages={979-985}, abstract={Network Function Virtualization (NFV) is considered one of the key technologies for the 5G mobile networks. In NFV, network functions are implemented in software components denominated Virtual Network Functions (VNFs) running on commodity hardware. In this paper, we propose an analytical model based on an open queuing network of G/G/m queues to model VNFs with several components, and chains of VNFs. Our model is flexible and generic enough to capture the behavior of such systems. We validate our model by simulation. Specifically, we validate it for an LTE virtualized Mobility Management Entity with a three-tiered architecture use case. We also compare our model with the estate of the art, in terms of computational complexity and estimation error. The results show that our model has a computational complexity similar to the method for analyzing Jackson's networks. Additionally, our model exhibits an estimation error, measured as the relative error for the estimation of the mean response time, approximately equal to 10%, whereas for the considered baseline systems it ranges roughly from 60% to 90%.}, keywords={Computational modeling;Analytical models;Iron;5G mobile communication;Computer architecture;Time factors;Queueing analysis;5G;NFV;VNF;analytical model;queuing model}, doi={10.1109/ICCW.2017.7962786}, ISSN={2474-9133}, month={May}, project={5gcity}
}
close
Optimized LTE data transmission procedures for IoT: Device side energy consumption analysis2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), pp. 540-545, May 2017, DOI: 10.1109/ICCW.2017.7962714.
"Optimized LTE data transmission procedures for IoT: Device side energy consumption analysis", P. Andres-Maldonado, P. Ameigeiras, J. Prados-Garzon, J. J. Ramos-Munoz, J. M. Lopez-Soler, "2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops)", pp. 540-545, 2017. DOI: 10.1109/ICCW.2017.7962714close
The efficient deployment of Internet of Things (IoT) over cellular networks, such as Long Term Evolution (LTE) or the next generation 5G, entails several challenges. For massive IoT, reducing the energy consumption on the device side becomes essential. One of the main characteristics of massive IoT is small data transmissions. To improve the support of them, the 3GPP has included two novel optimizations in LTE: one of them based on the Control Plane (CP), and the other on the User Plane (UP). In this paper, we analyze the average energy consumption per data packet using these two optimizations compared to conventional LTE Service Request procedure. We propose an analytical model to calculate the energy consumption for each procedure based on a Markov chain. In the considered scenario, for large and small Inter-Arrival Times (IATs), the results of the three procedures are similar. While for medium IATs CP reduces the energy consumption per packet up to 87% due to its connection release optimization.close
@INPROCEEDINGS{7962714, author={P. {Andres-Maldonado} and P. {Ameigeiras} and J. {Prados-Garzon} and J. J. {Ramos-Munoz} and J. M. {Lopez-Soler}}, booktitle={2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops)}, title={Optimized LTE data transmission procedures for IoT: Device side energy consumption analysis}, year={2017}, volume={}, number={}, pages={540-545}, abstract={The efficient deployment of Internet of Things (IoT) over cellular networks, such as Long Term Evolution (LTE) or the next generation 5G, entails several challenges. For massive IoT, reducing the energy consumption on the device side becomes essential. One of the main characteristics of massive IoT is small data transmissions. To improve the support of them, the 3GPP has included two novel optimizations in LTE: one of them based on the Control Plane (CP), and the other on the User Plane (UP). In this paper, we analyze the average energy consumption per data packet using these two optimizations compared to conventional LTE Service Request procedure. We propose an analytical model to calculate the energy consumption for each procedure based on a Markov chain. In the considered scenario, for large and small Inter-Arrival Times (IATs), the results of the three procedures are similar. While for medium IATs CP reduces the energy consumption per packet up to 87% due to its connection release optimization.}, keywords={Long Term Evolution;Energy consumption;Optimization;Data communication;3GPP;Context;Security}, doi={10.1109/ICCW.2017.7962714}, ISSN={2474-9133}, month={May}, project={5gcity}, pdf={https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/68238}
}
close
Diseno y evaluacion de un servicio OpenFlow de provision de Calidad de Experiencia sobre MininetXIII Jornadas de Ingenieria Telematica (JITEL 2017), 2017.
"Diseno y evaluacion de un servicio OpenFlow de provision de Calidad de Experiencia sobre Mininet", Cristian Prieto Sanchez, P. Maldonado, Jonathan Prados Garzon, J. Ramos-Munoz, "XIII Jornadas de Ingenieria Telematica (JITEL 2017)", 2017close
@inproceedings{Snchez2017DiseoYE,
title={Diseno y evaluacion de un servicio OpenFlow de provision de Calidad de Experiencia sobre Mininet},
booktitle={XIII Jornadas de Ingenieria Telematica (JITEL 2017)},
author={Cristian Prieto Sanchez and P. Maldonado and Jonathan Prados Garzon and J. Ramos-Munoz},
year={2017}, project={5gcity}, pdf={https://riunet.upv.es/handle/10251/101930}
}
close
Ph.D. Thesis
-
Management and Orchestration of Network Slicing in Public-Private 5G Networks
Defended on October 2022, ISBN 978-84-1117-566-1.
"Management and Orchestration of Network Slicing in Public-Private 5G Networks", Jose Antonio Ordonez-Lucena, University of Granada, ISBN 978-84-1117-566-1, 2022
close
@PhdThesis{thesisordonez,
author = {Jose Antonio Ordonez-Lucena},
director = {Pablo Ameigeiras},
title = {Management and Orchestration of Network Slicing in Public-Private 5G Networks},
institution = {University of Granada},
type = {phdthesis},
project = {5gcity|5gclarity|true5g|6gchronos},
year = {2022},
month = {October},
isbn = {978-84-1117-566-1},
pagetotal = {321},
pdf = {https://digibug.ugr.es/bitstream/handle/10481/77685/79489%281%29.pdf}
}
close
-
Network Slicing Management for 5G Radio Access Networks
Defended on April 2022, ISBN 978-84-1117-337-7.
"Network Slicing Management for 5G Radio Access Networks", Oscar Adamuz-Hinojosa, University of Granada, ISBN 978-84-1117-337-7, 2022
close
@PhdThesis{thesisadamuz,
author = {Oscar Adamuz-Hinojosa},
director = {Pablo Ameigeiras and Juan M. Lopez-Soler},
title = {Network Slicing Management for 5G Radio Access Networks},
institution = {University of Granada},
type = {phdthesis},
project = {5gcity|5gclarity|true5g|6gchronos},
year = {2022},
type = {phdthesis},
language = {English},
month = {April},
isbn = {978-84-1117-337-7},
pagetotal = {380},
pdf = {https://digibug.ugr.es/bitstream/handle/10481/74957/80783%281%29.pdf}
}
close
-
NB-IoT M2M communications in 5G cellular networks
Defended on April 2019, ISBN 978-84-1306-288-4.
"NB-IoT M2M communications in 5G cellular networks", Pilar Andres-Maldonado, University of Granada, ISBN 978-84-1306-288-4, 2019
close
@PhdThesis{thesisandres19,
author = {Pilar Andres-Maldonado},
director = {Juan M. Lopez-Soler and Pablo Ameigeiras},
title = {NB-IoT M2M communications in 5G cellular networks},
institution = {University of Granada},
year = {2019},
month = April,
type = {phdthesis},
language = {English},
isbn = {978-84-1306-288-4},
pagetotal = {286},
pdf = {https://digibug.ugr.es/bitstream/handle/10481/56821/67983.pdf},
project = {5gcity}
}
close
-
Architecture, modeling, planning, and dynamic provisioning of softwarized 5G mobile core networks
Defended on Sept. 2018, ISBN 978-84-1306-018-7.
"Architecture, modeling, planning, and dynamic provisioning of softwarized 5G mobile core networks", Jonathan Prados-Garzon, University of Granada, ISBN 978-84-1306-018-7, 2018
close
@PhdThesis{thesisprados18,
author = {Jonathan Prados-Garzon},
director = {Juan M. Lopez-Soler and Pablo Ameigeiras},
title = {Architecture, modeling, planning, and dynamic provisioning of softwarized 5G mobile core networks},
institution = {University of Granada},
year = {2018},
month = Sept.,
type = {phdthesis},
language = {English},
isbn = {978-84-1306-018-7},
pagetotal = {267},
pdf = {https://digibug.ugr.es/bitstream/handle/10481/53865/Jonathan%20Prados.pdf},
project = {5gcity}
}
close
Management and Orchestration of Network Slicing in Public-Private 5G NetworksDefended on October 2022, ISBN 978-84-1117-566-1."Management and Orchestration of Network Slicing in Public-Private 5G Networks", Jose Antonio Ordonez-Lucena, University of Granada, ISBN 978-84-1117-566-1, 2022close@PhdThesis{thesisordonez, author = {Jose Antonio Ordonez-Lucena}, director = {Pablo Ameigeiras}, title = {Management and Orchestration of Network Slicing in Public-Private 5G Networks}, institution = {University of Granada}, type = {phdthesis}, project = {5gcity|5gclarity|true5g|6gchronos}, year = {2022}, month = {October}, isbn = {978-84-1117-566-1}, pagetotal = {321}, pdf = {https://digibug.ugr.es/bitstream/handle/10481/77685/79489%281%29.pdf} }close@PhdThesis{thesisadamuz, author = {Oscar Adamuz-Hinojosa}, director = {Pablo Ameigeiras and Juan M. Lopez-Soler}, title = {Network Slicing Management for 5G Radio Access Networks}, institution = {University of Granada}, type = {phdthesis}, project = {5gcity|5gclarity|true5g|6gchronos}, year = {2022}, type = {phdthesis}, language = {English}, month = {April}, isbn = {978-84-1117-337-7}, pagetotal = {380}, pdf = {https://digibug.ugr.es/bitstream/handle/10481/74957/80783%281%29.pdf} }close@PhdThesis{thesisandres19, author = {Pilar Andres-Maldonado}, director = {Juan M. Lopez-Soler and Pablo Ameigeiras}, title = {NB-IoT M2M communications in 5G cellular networks}, institution = {University of Granada}, year = {2019}, month = April, type = {phdthesis}, language = {English}, isbn = {978-84-1306-288-4}, pagetotal = {286}, pdf = {https://digibug.ugr.es/bitstream/handle/10481/56821/67983.pdf}, project = {5gcity} }close@PhdThesis{thesisprados18, author = {Jonathan Prados-Garzon}, director = {Juan M. Lopez-Soler and Pablo Ameigeiras}, title = {Architecture, modeling, planning, and dynamic provisioning of softwarized 5G mobile core networks}, institution = {University of Granada}, year = {2018}, month = Sept., type = {phdthesis}, language = {English}, isbn = {978-84-1306-018-7}, pagetotal = {267}, pdf = {https://digibug.ugr.es/bitstream/handle/10481/53865/Jonathan%20Prados.pdf}, project = {5gcity} }close

